Essential role for retinoic acid in the promotion of CD4(+) T cell effector responses via retinoic acid receptor alpha
- PMID: 21419664
- PMCID: PMC3415227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.03.003
Essential role for retinoic acid in the promotion of CD4(+) T cell effector responses via retinoic acid receptor alpha
Abstract
Vitamin A and its metabolite, retinoic acid (RA) are implicated in the regulation of immune homeostasis via the peripheral induction of regulatory T cells. Here we showed RA was also required to elicit proinflammatory CD4(+) helper T cell responses to infection and mucosal vaccination. Retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARα) was the critical mediator of these effects. Antagonism of RAR signaling and deficiency in RARα (Rara(-/-)) resulted in a cell-autonomous CD4(+) T cell activation defect, which impaired intermediate signaling events, including calcium mobilization. Altogether, these findings reveal a fundamental role for the RA-RARα axis in the development of both regulatory and inflammatory arms of adaptive immunity and establish nutritional status as a broad regulator of adaptive T cell responses.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
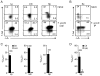
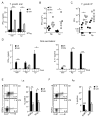
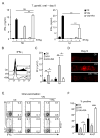
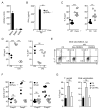
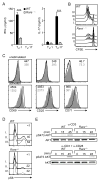
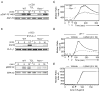
Comment in
-
Eat your carrots! T cells are RARing to go.Immunity. 2011 Mar 25;34(3):290-2. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.03.007. Immunity. 2011. PMID: 21435583
References
-
- Biesalski HK, Nohr D. New aspects in vitamin a metabolism: the role of retinyl esters as systemic and local sources for retinol in mucous epithelia. J Nutr. 2004;134:3453S–3457S. - PubMed
-
- Cantorna MT, Nashold FE, Hayes CE. In vitamin A deficiency multiple mechanisms establish a regulatory T helper cell imbalance with excess Th1 and insufficient Th2 function. J Immunol. 1994;152:1515–1522. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

