Complement inhibition alleviates paraquat-induced acute lung injury
- PMID: 21421909
- PMCID: PMC5460894
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0444OC
Complement inhibition alleviates paraquat-induced acute lung injury
Abstract
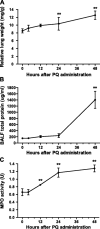
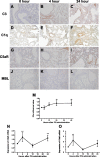
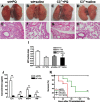
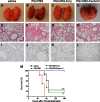
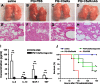
The widely used herbicide, paraquat (PQ), is highly toxic and claims thousands of lives from both accidental and voluntary ingestion. The pathological mechanisms of PQ poisoning-induced acute lung injury (ALI) are not well understood, and the role of complement in PQ-induced ALI has not been elucidated. We developed and characterized a mouse model of PQ-induced ALI and studied the role of complement in the pathogenesis of PQ poisoning. Intraperitoneal administration of PQ caused dose- and time-dependent lung damage and mortality, with associated inflammatory response. Within 24 hours of PQ-induced ALI, there was significantly increased expression of the complement proteins, C1q and C3, in the lung. Expression of the anaphylatoxin receptors, C3aR and C5aR, was also increased. Compared with wild-type mice, C3-deficient mice survived significantly longer and displayed significantly reduced lung inflammation and pathology after PQ treatment. Similar reductions in PQ-induced inflammation, pathology, and mortality were recorded in mice treated with the C3 inhibitors, CR2-Crry, and alternative pathway specific CR2-fH. A similar therapeutic effect was also observed by treatment with either C3a receptor antagonist or a blocking C5a receptor monoclonal antibody. Together, these studies indicate that PQ-induced ALI is mediated through receptor signaling by the C3a and C5a complement activation products that are generated via the alternative complement pathway, and that complement inhibition may be an effective clinical intervention for postexposure treatment of PQ-induced ALI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complement and the alternative pathway play an important role in LPS/D-GalN-induced fulminant hepatic failure.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e26838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026838. Epub 2011 Nov 1. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22069473 Free PMC article.
-
Doxycycline alleviates paraquat-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting neutrophil-derived matrix metalloproteinase 9.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Jul;72:243-251. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.04.015. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31003001
-
Inhibition of complement activation alleviates acute lung injury induced by highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus infection.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Aug;49(2):221-30. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0428OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23526211
-
Role of C3, C5 and anaphylatoxin receptors in acute lung injury and in sepsis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;946:147-59. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0106-3_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 21948367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of abnormal expression of signaling pathways in PQ-induced acute lung injury in SD rats based on RNA-seq technology.Inhal Toxicol. 2024 Jan;36(1):1-12. doi: 10.1080/08958378.2023.2300373. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Inhal Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38175690 Review.
Cited by
-
Blockade of the C5a-C5aR axis alleviates lung damage in hDPP4-transgenic mice infected with MERS-CoV.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2018 Apr 24;7(1):77. doi: 10.1038/s41426-018-0063-8. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2018. PMID: 29691378 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the anaphylatoxin receptors, C3aR and C5aR, to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis.FASEB J. 2016 Jun;30(6):2336-50. doi: 10.1096/fj.201500044. Epub 2016 Mar 8. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26956419 Free PMC article.
-
Donor pretreatment with nebulized complement C3a receptor antagonist mitigates brain-death induced immunological injury post-lung transplant.Am J Transplant. 2018 Oct;18(10):2417-2428. doi: 10.1111/ajt.14717. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Am J Transplant. 2018. PMID: 29504277 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of soluble CD14 subtype on the prognosis evaluation of acute paraquat poisoning patients.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Oct 1;10(10):10392-10398. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966375 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting complement anaphylatoxin C5a receptor in hyperoxic lung injury in mice.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Oct;10(4):1786-92. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2394. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 25050483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Onyeama HP, Oehme FW. A literature review of paraquat toxicity. Vet Hum Toxicol 1984;26:494–502. - PubMed
-
- Chan BS, Lazzaro VA, Seale JP, Duggin GG. The renal excretory mechanisms and the role of organic cations in modulating the renal handling of paraquat. Pharmacol Ther 1998;79:193–203. - PubMed
-
- Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Remiao F, Carmo H, Duarte JA, Navarro AS, Bastos ML, Carvalho F. Paraquat exposure as an etiological factor of Parkinson's disease. Neurotoxicology 2006;27:1110–1122. - PubMed
-
- Dinis-Oliveira RJ, De Jesus Valle MJ, Bastos ML, Carvalho F, Sanchez Navarro A. Kinetics of paraquat in the isolated rat lung: influence of sodium depletion. Xenobiotica 2006;36:724–737. - PubMed
-
- Sittipunt C. Paraquat poisoning. Respir Care 2005;50:383–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

