Graft-versus-host disease is the major determinant of humoral responses to the AS03-adjuvanted influenza A/09/H1N1 vaccine in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients
- PMID: 21422117
- PMCID: PMC3105652
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2011.040386
Graft-versus-host disease is the major determinant of humoral responses to the AS03-adjuvanted influenza A/09/H1N1 vaccine in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients
Abstract
Background: Responses to influenza vaccines are poorly characterized in immunocompromised patients. The goal of this study was to assess the efficacy of the AS03-adjuvanted influenza H1N1/A/09 vaccine in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients.
Design and methods: We enrolled 65 patients and 138 controls in an open prospective study. Controls received one dose and patients 2 doses of the AS03-adjuvanted influenza H1N1/A/09 vaccine at a 3-week interval. Geometric mean titers and seroprotection/seroconversion rates were determined by hemagglutination inhibition before and four weeks after the last immunization. Clinical and biological markers, including immunoglobulins, CD3+, CD4+, CD8+ and naïve CD4+ T-cell counts were assessed in all patients.
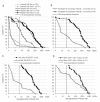
Results: Baseline seroprotection rates were low in patients (6.6%) and controls (14.8%). After 2 doses, patients (n=57, 92.3%) achieved similar seroprotection rates (84% vs. 87%, P=0.65) and antibody titers (305 vs. 340, P=0.88) as controls (n=131, 93.9%) after one dose. In univariate analysis, transplant-to-vaccination interval less than 12 months, active graft-versus-host disease, immunosuppressive drugs, hemoglobin less than 12 g/L, lymphopenia less than 1 G/L, IgG less than 4 g/L, IgA less than 0.5 g/L, IgM less than 0.5 g/L and naive CD4+ T cells less than 150/μL were significantly associated with weaker responses. Multivariate analysis identified transplant-to-vaccination interval and active graft-versus-host disease as the most powerful negative predictors of antibody responses (P=0.04 and P=0.002, respectively). Vaccination was well tolerated in both cohorts.
Conclusions: In allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients, 2 doses of an adjuvanted influenza vaccine elicited comparable responses to a single dose in healthy individuals. However, vaccine responses remained poor in patients with ongoing graft-versus-host disease, supporting the need for additional strategies in this high-risk patient population. (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01022905).
Figures
References
-
- Martino R, Porras RP, Rabella N, Williams JV, Ramila E, Margall N, et al. Prospective study of the incidence, clinical features, and outcome of symptomatic upper and lower respiratory tract infections by respiratory viruses in adult recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplants for hematologic malignancies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005;11(10):781–96. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ljungman P, Ward KN, Crooks BN, Parker A, Martino R, Shaw PJ, et al. Respiratory virus infections after stem cell transplantation: a prospective study from the Infectious Diseases Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001;28(5):479–84. - PubMed
-
- Nichols WG, Guthrie KA, Corey L, Boeckh M. Influenza infections after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: risk factors, mortality, and the effect of antiviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39(9):1300–6. - PubMed
-
- Khanna N, Steffen I, Studt JD, Schreiber A, Lehmann T, Weisser M, et al. Outcome of influenza infections in outpatients after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis. 2009;11(2):100–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

