Convergence of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1- and glycogen synthase kinase 3-β-signaling pathways regulates the innate inflammatory response
- PMID: 21422248
- PMCID: PMC3137265
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002513
Convergence of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1- and glycogen synthase kinase 3-β-signaling pathways regulates the innate inflammatory response
Abstract
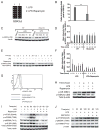
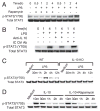
The PI3K pathway and its regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) and glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) play pivotal roles in controlling inflammation. In this article, we show that mTORC1 and GSK3-β converge and that the capacity of mTORC1 to affect the inflammatory response is due to the inactivation of GSK3-β. Inhibition of mTORC1 attenuated GSK3 phosphorylation and increased its kinase activity. Immunoprecipitation and in vitro kinase assays demonstrated that GSK3-β associated with a downstream target of mTORC1, p85S6K, and phosphorylated GSK3-β. Inhibition of S6K1 abrogated the phosphorylation of GSK3-β while increasing and decreasing the levels of IL-12 and IL-10, respectively, in LPS-stimulated monocytes. In contrast, the direct inhibition of GSK3 attenuated the capacity of S6K1 inhibition to influence the levels of IL-10 and IL-12 produced by LPS-stimulated cells. At the transcriptional level, mTORC1 inhibition reduced the DNA binding of CREB and this effect was reversed by GSK3 inhibition. As a result, mTORC1 inhibition increased the levels of NF-κB p65 associated with CREB-binding protein. Inhibition of NF-κB p65 attenuated rapamycin's ability to influence the levels of pro- or anti-inflammatory cytokine production in monocytes stimulated with LPS. These studies identify the molecular mechanism by which mTORC1 affects GSK3 and show that mTORC1 inhibition regulates pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine production via its capacity to inactivate GSK3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The role of JAK-3 in regulating TLR-mediated inflammatory cytokine production in innate immune cells.J Immunol. 2013 Aug 1;191(3):1164-74. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203084. Epub 2013 Jun 24. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23797672 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 involvement in the excessive proinflammatory response to LPS in patients with decompensated cirrhosis.J Hepatol. 2011 Oct;55(4):784-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.12.039. Epub 2011 Feb 18. J Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21334395
-
TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-1 expression is inhibited by GAS6 in monocytes/macrophages.J Leukoc Biol. 2010 May;87(5):869-75. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0909610. Epub 2010 Jan 26. J Leukoc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20103767
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3: a point of convergence for the host inflammatory response.Cytokine. 2011 Feb;53(2):130-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2010.10.009. Epub 2010 Nov 23. Cytokine. 2011. PMID: 21095632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate and adaptive immune responses regulated by glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3).Trends Immunol. 2010 Jan;31(1):24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2009.09.007. Epub 2009 Oct 14. Trends Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19836308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological inhibition of PI3K class III enhances the production of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in dendritic cells stimulated by TLR agonists.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Jul;36:213-217. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.04.028. Epub 2016 May 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27168056 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Muscle Fatigue.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 27;22(21):11587. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111587. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation by glycogen synthase kinase-3 of inflammation and T cells in CNS diseases.Front Mol Neurosci. 2011 Aug 31;4:18. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2011.00018. eCollection 2011. Front Mol Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21941466 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3: A Focal Point for Advancing Pathogenic Inflammation in Depression.Cells. 2021 Sep 1;10(9):2270. doi: 10.3390/cells10092270. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Hydrogen Sulfide in Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury.Biomolecules. 2024 Jun 22;14(7):740. doi: 10.3390/biom14070740. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062455 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Janeway CA., Jr A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature. 1997;388:394–397. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Kopp E, Stadlen A, Chen C, Ghosh S, Janeway CA., Jr MyD88 is an adaptor protein in the hToll/IL-1 receptor family signaling pathways. Mol Cell. 1998;2:253–258. - PubMed
-
- Yang RB, Mark MR, Gray A, Huang A, Xie MH, Zhang M, Goddard A, Wood WI, Gurney AL, Godowski PJ. Toll-like receptor-2 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced cellular signalling. Nature. 1998;395:284–288. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. TLR signaling. Semin Immunol. 2007;19:24–32. - PubMed
-
- Kumar H, Kawai T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;388:621–625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

