Population incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 21422765
- PMCID: PMC5703046
- DOI: 10.1159/000324710
Population incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
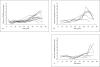
Population incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is required to assess changes in GBS epidemiology, but published estimates of GBS incidence vary greatly depending on case ascertainment, definitions, and sample size. We performed a meta-analysis of articles on GBS incidence by searching Medline (1966-2009), Embase (1988-2009), Cinahl (1981-2009) and CABI (1973-2009) as well as article bibliographies. We included studies from North America and Europe with at least 20 cases, and used population-based data, subject matter experts to confirm GBS diagnosis, and an accepted GBS case definition. With these data, we fitted a random-effects negative binomial regression model to estimate age-specific GBS incidence. Of 1,683 nonduplicate citations, 16 met the inclusion criteria, which produced 1,643 cases and 152.7 million person-years of follow-up. GBS incidence increased by 20% for every 10-year increase in age; the risk of GBS was higher for males than females. The regression equation for calculating the average GBS rate per 100,000 person-years as a function of age in years was exp[-12.0771 + 0.01813(age in years)] × 100,000. Our findings provide a robust estimate of background GBS incidence in Western countries. Our regression model may be used in comparable populations to estimate the background age-specific rate of GBS incidence for future studies.
Copyright © 2011 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

References
-
- Hughes RA, Cornblath DR. Guillain-Barre syndrome. Lancet. 2005;366:1653–1666. - PubMed
-
- Hughes RA, Hadden RD, Gregson NA, Smith KJ. Pathogenesis of Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neuroimmunol. 1999;100:74–97. - PubMed
-
- Levin MC, Krichavsky M, Berk J, Foley S, Rosenfeld M, Dalmau J, Chang G, Posner JB, Jacobson S. Neuronal molecular mimicry in immune-mediated neurologic disease. Ann Neurol. 1998;44:87–98. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura T. Infectious agents as the triggers for the pathogenesis of the neuroimmunological disorders. Nippon Rinsho. 2008;66:1056–1064. - PubMed
-
- Rees JH, Soudain SE, Gregson NA, Hughes RA. Campylobacter jejuni infection and Guillain-Barré syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1374–1379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

