MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins
- PMID: 21423178
- PMCID: PMC3074610
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210
MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins
Erratum in
- Nat Cell Biol. 2015 Jan;17(1):104
Abstract
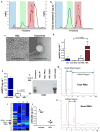
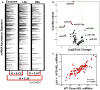
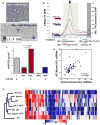
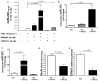
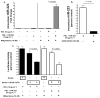
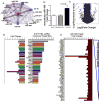
Circulating microRNAs (miRNA) are relatively stable in plasma and are a new class of disease biomarkers. Here we present evidence that high-density lipoprotein (HDL) transports endogenous miRNAs and delivers them to recipient cells with functional targeting capabilities. Cellular export of miRNAs to HDL was demonstrated to be regulated by neutral sphingomyelinase. Reconstituted HDL injected into mice retrieved distinct miRNA profiles from normal and atherogenic models. HDL delivery of both exogenous and endogenous miRNAs resulted in the direct targeting of messenger RNA reporters. Furthermore, HDL-mediated delivery of miRNAs to recipient cells was demonstrated to be dependent on scavenger receptor class B type I. The human HDL-miRNA profile of normal subjects is significantly different from that of familial hypercholesterolemia subjects. Notably, HDL-miRNA from atherosclerotic subjects induced differential gene expression, with significant loss of conserved mRNA targets in cultured hepatocytes. Collectively, these observations indicate that HDL participates in a mechanism of intercellular communication involving the transport and delivery of miRNAs.
© 2011 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Simons M, Raposo G. Exosomes--vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21:575–581. - PubMed
-
- Valadi H, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:654–659. - PubMed
-
- Ratajczak J, Wysoczynski M, Hayek F, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak MZ. Membrane-derived microvesicles: important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia. 2006;20:1487–1495. - PubMed
-
- Selbach M, et al. Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature. 2008;455:58–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

