A novel small molecule antagonist of choline kinase-α that simultaneously suppresses MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling
- PMID: 21423211
- PMCID: PMC3136659
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.51
A novel small molecule antagonist of choline kinase-α that simultaneously suppresses MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling
Abstract
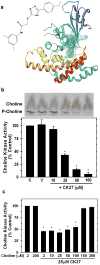
Choline kinase-α expression and activity are increased in multiple human neoplasms as a result of growth factor stimulation and activation of cancer-related signaling pathways. The product of choline kinase-α, phosphocholine, serves as an essential metabolic reservoir for the production of phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid constituent of membranes and substrate for the production of lipid second messengers. Using in silico screening for small molecules that may interact with the choline kinase-α substrate binding domain, we identified a novel competitive inhibitor, N-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)-2-[[5-(4-ethylphenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]sulfanyl] acetamide (termed CK37) that inhibited purified recombinant human choline kinase-α activity, reduced the steady-state concentration of phosphocholine in transformed cells, and selectively suppressed the growth of neoplastic cells relative to normal epithelial cells. Choline kinase-α activity is required for the downstream production of phosphatidic acid, a promoter of several Ras signaling pathways. CK37 suppressed mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT signaling, disrupted actin cytoskeletal organization, and reduced plasma membrane ruffling. Finally, administration of CK37 significantly decreased tumor growth in a lung tumor xenograft mouse model, suppressed tumor phosphocholine, and diminished activating phosphorylations of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and AKT in vivo. Together, these results further validate choline kinase-α as a molecular target for the development of agents that interrupt Ras signaling pathways, and indicate that receptor-based computational screening should facilitate the identification of new classes of choline kinase-α inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Selective inhibition of choline kinase simultaneously attenuates MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling.Oncogene. 2010 Jan 7;29(1):139-49. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.317. Epub 2009 Oct 26. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 19855431
-
Differential regulation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase and MAP kinase pathways by hepatocyte growth factor vs. insulin-like growth factor-I in myogenic cells.Exp Cell Res. 2004 Jul 1;297(1):224-34. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.03.024. Exp Cell Res. 2004. PMID: 15194438
-
K-RAS mutant pancreatic tumors show higher sensitivity to MEK than to PI3K inhibition in vivo.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44146. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044146. Epub 2012 Aug 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952903 Free PMC article.
-
Dual blockade of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR (AZD8055) and RAS/MEK/ERK (AZD6244) pathways synergistically inhibits rhabdomyosarcoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Nov 1;19(21):5940-51. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0850. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23918606 Free PMC article.
-
Concomitant activation of the PI3K-Akt and the Ras-ERK signaling pathways is essential for transformation by the V-SEA tyrosine kinase oncogene.Oncogene. 2002 Jan 24;21(5):697-707. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205115. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 11850798
Cited by
-
Choline Metabolism Alteration: A Focus on Ovarian Cancer.Front Oncol. 2016 Jun 22;6:153. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00153. eCollection 2016. Front Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27446799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel model based on lipid metabolism-related genes associated with immune microenvironment predicts metastasis of breast cancer.Discov Oncol. 2024 Aug 27;15(1):372. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01253-0. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39190262 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated choline metabolism in T-cell lymphoma: role of choline kinase-α and therapeutic targeting.Blood Cancer J. 2015 Mar 13;5(3):287. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2015.10. Blood Cancer J. 2015. PMID: 25768400 Free PMC article.
-
A functional siRNA screen identifies genes modulating angiotensin II-mediated EGFR transactivation.J Cell Sci. 2013 Dec 1;126(Pt 23):5377-90. doi: 10.1242/jcs.128280. Epub 2013 Sep 17. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 24046455 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Phospholipid Metabolism in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2016 Dec 27;6:266. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00266. eCollection 2016. Front Oncol. 2016. PMID: 28083512 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ackerstaff E, Glunde K, Bhujwalla ZM. Choline phospholipid metabolism: a target in cancer cells? J Cell Biochem. 2003;90:525–33. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama C, Liao H, Ishidate K. Structure and function of choline kinase isoforms in mammalian cells. Prog Lipid Res. 2004;43:266–81. - PubMed
-
- Chung T, Huang JS, Mukherjee JJ, Crilly KS, Kiss Z. Expression of human choline kinase in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts increases the mitogenic potential of insulin and insulin-like growth factor I. Cell Signal. 2000;12:279–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

