Combinatory action of VEGFR2 and MAP kinase pathways maintains endothelial-cell integrity
- PMID: 21423276
- PMCID: PMC3193492
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2011.41
Combinatory action of VEGFR2 and MAP kinase pathways maintains endothelial-cell integrity
Abstract
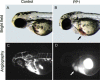
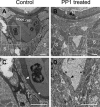
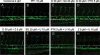
Blood vessels normally maintain stereotyped lumen diameters and their stable structures are crucial for vascular function. However, very little is known about the molecular mechanisms controlling the maintenance of vessel diameters and the integrity of endothelial cells. We investigated this issue in zebrafish embryos by a chemical genetics approach. Small molecule libraries were screened using live Tg(kdrl:GRCFP)(zn1) transgenic embryos in which endothelial cells are specifically labeled with GFP. By analyzing the effects of compounds on the morphology and function of embryonic blood vessels after lumen formation, PP1, a putative Src kinase inhibitor, was identified as capable of specifically reducing vascular lumen size by interrupting endothelial-cell integrity. The inhibitory effect is not due to Src or general VEGF signaling inhibition because another Src inhibitor and Src morpholino as well as several VEGFR inhibitors failed to produce a similar phenotype. After profiling a panel of 22 representative mammalian kinases and surveying published data, we selected a few possible new candidates. Combinational analysis of these candidate kinase inhibitors established that PP1 induced endothelial collapse by inhibiting both the VEGFR2 and MAP kinase pathways. More importantly, combinatory use of two clinically approved drugs Dasatinib and Sunitinib produced the same phenotype. This is the first study to elucidate the pathways controlling maintenance of endothelial integrity using a chemical genetics approach, indicating that endothelial integrity is controlled by the combined action of the VEGFR2 and MAP kinase pathways. Our results also suggest the possible side effect of the combination of two anticancer drugs on the circulatory system.
Figures


Similar articles
-
VEGFR2 and Src kinase inhibitors suppress Andes virus-induced endothelial cell permeability.J Virol. 2011 Mar;85(5):2296-303. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02319-10. Epub 2010 Dec 22. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21177802 Free PMC article.
-
c-Src mediates mitogenic signals and associates with cytoskeletal proteins upon vascular endothelial growth factor stimulation in Kaposi's sarcoma cells.J Immunol. 2000 Feb 1;164(3):1169-74. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.3.1169. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10640727
-
A dual inhibitor of platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor and Src kinase activity potently interferes with motogenic and mitogenic responses to PDGF in vascular smooth muscle cells. A novel candidate for prevention of vascular remodeling.Circ Res. 1999 Jul 9;85(1):12-22. doi: 10.1161/01.res.85.1.12. Circ Res. 1999. PMID: 10400906
-
Silica nanoparticles inhibit macrophage activity and angiogenesis via VEGFR2-mediated MAPK signaling pathway in zebrafish embryos.Chemosphere. 2017 Sep;183:483-490. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.138. Epub 2017 May 24. Chemosphere. 2017. PMID: 28570891
-
SKLB1002, a novel potent inhibitor of VEGF receptor 2 signaling, inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in vivo.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Jul 1;17(13):4439-50. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-3109. Epub 2011 May 27. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21622720
Cited by
-
UBIAD1-mediated vitamin K2 synthesis is required for vascular endothelial cell survival and development.Development. 2013 Apr;140(8):1713-9. doi: 10.1242/dev.093112. Development. 2013. PMID: 23533172 Free PMC article.
-
A distinct mechanism of vascular lumen formation in Xenopus requires EGFL7.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 23;10(2):e0116086. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116086. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25705891 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes disrupts the response of retinal endothelial cells to the angiomodulator lysophosphatidic acid.Diabetes. 2012 May;61(5):1225-33. doi: 10.2337/db11-1189. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22415872 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of CML TKI Induced Cardiovascular Toxicity and Development of Potential Rescue Strategies in a Zebrafish Model.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 18;12:740529. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.740529. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34733159 Free PMC article.
-
PDGF signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis pathogenesis and therapeutics (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2017 Dec;16(6):7879-7889. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7641. Epub 2017 Sep 27. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28983598 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kamei M, Saunders WB, Bayless KJ, Dye L, Davis GE, Weinstein BM. Endothelial tubes assemble from intracellular vacuoles in vivo. Nature. 2006;442:453–456. - PubMed
-
- Blum Y, Belting HG, Ellertsdottir E, Herwig L, Lüders F, Affolter M. Complex cell rearrangements during intersegmental vessel sprouting and vessel fusion in the zebrafish embryo. Dev Biol. 2008;316:312–322. - PubMed
-
- Ellertsdottir E, Lenard A, Blum Y, et al. Vascular morphogenesis in the zebrafish embryo. Dev Biol. 2010;341:56–65. - PubMed
-
- Strilic B, Kucera T, Eglinger J, et al. The molecular basis of vascular lumen formation in the developing mouse aorta. Dev Cell. 2009;17:505–515. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

