mRNA display selection of an optimized MDM2-binding peptide that potently inhibits MDM2-p53 interaction
- PMID: 21423613
- PMCID: PMC3057987
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017898
mRNA display selection of an optimized MDM2-binding peptide that potently inhibits MDM2-p53 interaction
Abstract
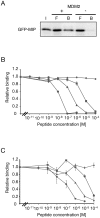
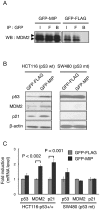
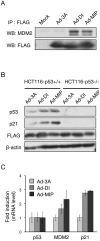
p53 is a tumor suppressor protein that prevents tumorigenesis through cell cycle arrest or apoptosis of cells in response to cellular stress such as DNA damage. Because the oncoprotein MDM2 interacts with p53 and inhibits its activity, MDM2-p53 interaction has been a major target for the development of anticancer drugs. While previous studies have used phage display to identify peptides (such as DI) that inhibit the MDM2-p53 interaction, these peptides were not sufficiently optimized because the size of the phage-displayed random peptide libraries did not cover all of the possible sequences. In this study, we performed selection of MDM2-binding peptides from large random peptide libraries in two stages using mRNA display. We identified an optimal peptide named MIP that inhibited the MDM2-p53 and MDMX-p53 interactions 29- and 13-fold more effectively than DI, respectively. Expression of MIP fused to the thioredoxin scaffold protein in living cells by adenovirus caused stabilization of p53 through its interaction with MDM2, resulting in activation of the p53 pathway. Furthermore, expression of MIP also inhibited tumor cell proliferation in a p53-dependent manner more potently than DI. These results show that two-stage, mRNA-displayed peptide selection is useful for the rapid identification of potent peptides that target oncoproteins.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


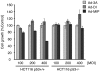
Similar articles
-
Structural basis for inhibition of the MDM2:p53 interaction by an optimized MDM2-binding peptide selected with mRNA display.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 2;9(10):e109163. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109163. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25275651 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for high-affinity peptide inhibition of p53 interactions with MDM2 and MDMX.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Mar 24;106(12):4665-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900947106. Epub 2009 Mar 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19255450 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient p53 activation and apoptosis by simultaneous disruption of binding to MDM2 and MDMX.Cancer Res. 2007 Sep 15;67(18):8810-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1140. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17875722
-
How To Design a Successful p53-MDM2/X Interaction Inhibitor: A Thorough Overview Based on Crystal Structures.ChemMedChem. 2016 Apr 19;11(8):757-72. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201500487. Epub 2015 Dec 16. ChemMedChem. 2016. PMID: 26676832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The past, present and future of potential small-molecule drugs targeting p53-MDM2/MDMX for cancer therapy.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Aug 15;176:92-104. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.05.018. Epub 2019 May 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31100649 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterizing the conformational landscape of MDM2-binding p53 peptides using Molecular Dynamics simulations.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 15;7(1):15600. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15930-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29142290 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus evades the immune system by suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway with DENND2A.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Mar 5;12(3):e0378523. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03785-23. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38240571 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for inhibition of the MDM2:p53 interaction by an optimized MDM2-binding peptide selected with mRNA display.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 2;9(10):e109163. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109163. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25275651 Free PMC article.
-
Translation of Deoxyribonucleic Acid into Synthetic Alpha Helical Peptides for Darwinian Evolution.JACS Au. 2024 Oct 2;4(10):4013-4022. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.4c00738. eCollection 2024 Oct 28. JACS Au. 2024. PMID: 39483244 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of Peptide Library in Mammalian Cells by dsDNA-Based Strategy.ACS Omega. 2022 Dec 29;8(1):1037-1046. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c06402. eCollection 2023 Jan 10. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36643544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chene P. Inhibiting the p53-MDM2 interaction: an important target for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:102–109. - PubMed
-
- Meek DW. Tumor suppression by p53: a role for the DNA damage response? Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:714–723. - PubMed
-
- Wasylyk C, Salvi R, Argentini M, Dureuil C, Abecassis J, et al. p53 mediated death of cells overexpressing MDM2 by an inhibitor of MDM2 interaction with p53. Oncogene. 1999;18:1921–1934. - PubMed
-
- Chene P. Inhibiting the p53-MDM2 interaction: an important target for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:102–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

