Predicting pancreas cell fate decisions and reprogramming with a hierarchical multi-attractor model
- PMID: 21423725
- PMCID: PMC3056652
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014752
Predicting pancreas cell fate decisions and reprogramming with a hierarchical multi-attractor model
Abstract
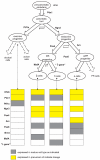
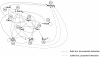
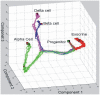
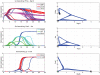
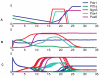
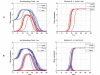
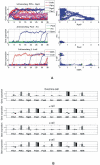
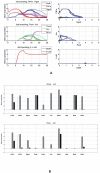
Cell fate reprogramming, such as the generation of insulin-producing β cells from other pancreas cells, can be achieved by external modulation of key transcription factors. However, the known gene regulatory interactions that form a complex network with multiple feedback loops make it increasingly difficult to design the cell reprogramming scheme because the linear regulatory pathways as schemes of causal influences upon cell lineages are inadequate for predicting the effect of transcriptional perturbation. However, sufficient information on regulatory networks is usually not available for detailed formal models. Here we demonstrate that by using the qualitatively described regulatory interactions as the basis for a coarse-grained dynamical ODE (ordinary differential equation) based model, it is possible to recapitulate the observed attractors of the exocrine and β, δ, α endocrine cells and to predict which gene perturbation can result in desired lineage reprogramming. Our model indicates that the constraints imposed by the incompletely elucidated regulatory network architecture suffice to build a predictive model for making informed decisions in choosing the set of transcription factors that need to be modulated for fate reprogramming.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Davidson EH, Erwin DH. Gene regulatory networks and the evolution of animal body plans. Science. 2006;311:796–800. - PubMed
-
- Huang S, Eichler G, Bar-Yam Y, Ingber DE. Cell fates as high-dimensional attractor states of a complex gene regulatory network. Phys Rev Lett. 2005;94:128701. - PubMed
-
- Huang S. Reprogramming cell fates: reconciling rarity with robustness. Bioessays. 2009;31:546–560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

