Abnormal production of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines by lupus monocytes in response to apoptotic cells
- PMID: 21423726
- PMCID: PMC3056659
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017495
Abnormal production of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines by lupus monocytes in response to apoptotic cells
Abstract
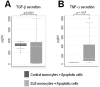
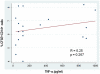
Monocytes are a key component of the innate immune system involved in the regulation of the adaptive immune response. Previous studies have focused on apoptotic cell clearance abnormalities in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) monocytes. However, whether SLE monocytes might express unique patterns of cytokine secretion in response to apoptotic cells is still unknown. Here, we used monocytes from healthy controls and SLE patients to evaluate the production of TNF-α and TGF-β in response to apoptotic cells. Upon recognition of apoptotic material, monocytes from healthy controls showed prominent TGF-β secretion (mean ± SD: 824.6±144.3 pg/ml) and minimal TNF-α production (mean ± SD: 32.6±2.1 pg/ml). In contrast, monocytes from SLE patients had prominent TNF-α production (mean ± SD: 302.2±337.5 pg/ml) and diminished TGF-β secretion (mean ± SD: 685.9±615.9 pg/ml), a difference that was statistically significant compared to normal monocytes (p≤10(-6) for TNF-α secretion, and p = 0.0031 for TGF-β, respectively). Interestingly, the unique cytokine response by SLE monocytes was independent of their phagocytic clearance efficiency, opsonizing autoantibodies and disease activity. We further showed that nucleic acids from apoptotic cells play important role in the induction of TNF-α by lupus monocytes. Together, these observations suggest that, in addition to potential clearance defects, monocytes from SLE patients have an abnormal balance in the secretion of anti- and pro-inflammatory cytokines in response to apoptotic cells. Since the abnormal cytokine response to apoptotic material in SLE is not related to disease activity and opsonizing autoantibodies, it is possible that this response might be an intrinsic property of lupus monocytes. The studies focus attention on toll-like receptors (TLRs) and their downstream pathways as mediators of this response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of the impairment of the uptake of apoptotic polymorphonuclear cells by monocyte subpopulations in systemic lupus erythematosus.Lupus. 2014 Nov;23(13):1358-69. doi: 10.1177/0961203314541316. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Lupus. 2014. PMID: 24969081
-
Increased apoptotic neutrophils and macrophages and impaired macrophage phagocytic clearance of apoptotic neutrophils in systemic lupus erythematosus.Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Oct;48(10):2888-97. doi: 10.1002/art.11237. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 14558095
-
Transcriptional and translational regulation of inflammatory mediator production by endogenous TGF-beta in macrophages that have ingested apoptotic cells.J Immunol. 1999 Dec 1;163(11):6164-72. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10570307
-
Genetics of SLE: functional relevance for monocytes/macrophages in disease.Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:582352. doi: 10.1155/2012/582352. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23227085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory clearance of apoptotic remnants in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).Autoimmun Rev. 2008 Oct;8(1):9-12. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2008.07.015. Epub 2008 Aug 12. Autoimmun Rev. 2008. PMID: 18703173 Review.
Cited by
-
SIGN-R1, a C-type lectin, enhances apoptotic cell clearance through the complement deposition pathway by interacting with C1q in the spleen.Cell Death Differ. 2013 Apr;20(4):535-45. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2012.160. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Cell Death Differ. 2013. PMID: 23238564 Free PMC article.
-
Immune infiltration analysis reveals immune cell signatures in salivary gland tissue of primary Sjögren's syndrome.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 18;10:1033232. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1033232. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36744136 Free PMC article.
-
The role of probiotics in promoting systemic immune tolerance in systemic lupus erythematosus.Gut Pathog. 2025 Jun 17;17(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13099-025-00702-7. Gut Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40528248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose Tissue Immunometabolism and Apoptotic Cell Clearance.Cells. 2021 Sep 2;10(9):2288. doi: 10.3390/cells10092288. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic lupus Erythematosus activity and Hydroxychloroquine use before and after end-stage renal disease.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):450. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-02083-2. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 33115441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shlomchik MJ, Craft JE, Mamula MJ. From T to B and back again: positive feedback in systemic autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1:147–153. - PubMed
-
- Andrade F, Casciola-Rosen L, Rosen A. Apoptosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical implications. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2000;26:215–27. - PubMed
-
- Voll RE, Herrmann M, Roth EA, Stach C, Kalden JR, et al. Immunosuppressive effects of apoptotic cells. Nature. 1997;390:350–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

