Cellular fibronectin stimulates hepatocytes to produce factors that promote alcohol-induced liver injury
- PMID: 21423914
- PMCID: PMC3060416
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v3.i2.45
Cellular fibronectin stimulates hepatocytes to produce factors that promote alcohol-induced liver injury
Abstract
Aim: To examine the consequences of cellular fibronectin (cFn) accumulation during alcohol-induced injury, and investigate whether increased cFn could have an effect on hepatocytes (HCs) by producing factors that could contribute to alcohol-induced liver injury.
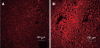
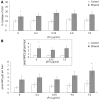
Methods: HCs were isolated from rats fed a control or ethanol liquid diet for four to six weeks. Exogenous cFn (up to 7.5 μg/mL) was added to cells cultured for 20 h, and viability (lactate dehydrogenase,LDH), apoptosis (caspase activity) and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor alpha, TNF-α and interleukin 6 IL-6), matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors (tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases, TIMPs) was determined. Degradation of iodinated cFn was determined over a 3 h time period in the preparations.
Results: cFn degradation is impaired in HCs isolated from ethanol-fed animals, leading to its accumulation in the matrix. Addition of exogenous cFn did not affect viability of HCs from control or ethanol-fed animals, and apoptosis was affected only at the higher concentration. Secretion of MMPs, TIMPs, TNF-α and IL-6, however, was increased by exogenously added cFn, with HCs from ethanol-fed animals showing increased susceptibility compared to the controls.
Conclusion: These results suggest that the elevated amounts of cFn observed in alcoholic liver injury can stimulate hepatocytes to produce factors which promote further tissue damage.
Keywords: Alcoholic liver diseases; Asialoglycoprotein receptor; Fibronectin; Fibrosis; Hepatocytes; Inflammation.
Figures
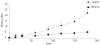



Similar articles
-
Ethanol feeding potentiates the pro-inflammatory response of Kupffer cells to cellular fibronectin.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011 Apr;35(4):717-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01389.x. Epub 2011 Jan 11. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011. PMID: 21223308
-
Deposition of cellular fibronectin increases before stellate cell activation in rat liver during ethanol feeding.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1997 Aug;21(5):857-61. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1997. PMID: 9267535
-
Fibronectin: functional character and role in alcoholic liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 May 28;17(20):2482-99. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i20.2482. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21633653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rat pancreatic stellate cells secrete matrix metalloproteinases: implications for extracellular matrix turnover.Gut. 2003 Feb;52(2):275-82. doi: 10.1136/gut.52.2.275. Gut. 2003. PMID: 12524413 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired receptor-mediated endocytosis: its role in alcohol-induced apoptosis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008 Mar;23 Suppl 1:S46-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.05275.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 18336663 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunomodulatory Role of the Extracellular Matrix Within the Liver Disease Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 11;11:574276. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.574276. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33262757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic analysis of plasma proteins during fentanyl withdrawal in ovariectomized female rats with and without estradiol.J Neuroendocrinol. 2025 Aug;37(8):e70033. doi: 10.1111/jne.70033. Epub 2025 Apr 20. J Neuroendocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40254411 Free PMC article.
-
Defects in MAP1S-mediated autophagy cause reduction in mouse lifespans especially when fibronectin is overexpressed.Aging Cell. 2016 Apr;15(2):370-9. doi: 10.1111/acel.12441. Epub 2016 Jan 10. Aging Cell. 2016. PMID: 26750654 Free PMC article.
-
Transitional Remodeling of the Hepatic Extracellular Matrix in Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:3162670. doi: 10.1155/2016/3162670. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27843941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping Tumor-Stroma-ECM Interactions in Spatially Advanced 3D Models of Pancreatic Cancer.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Mar 19;17(11):16708-16724. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c02296. Epub 2025 Mar 7. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40052705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mailliard ME, Sorrell MF, Volentine GD, Tuma DJ. Impaired plasma membrane glycoprotein assembly in the liver following acute ethanol administration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984;123:951–982. - PubMed
-
- Sorrell MF, Nauss JM, Donohue TM Jr, Tuma DJ. Effects of chronic ethanol administration on hepatic glycoprotein secretion in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1983;84:580–586. - PubMed
-
- Tuma DJ, Casey CA, Sorrell MF. Effects of alcohol on hepatic protein metabolism and trafficking. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl. 1991;1:297–303. - PubMed
-
- Casey CA, Sorrel MF, Tuma DJ. Effect of Ethanol on Asialoglycoprotein Receptor Function. In: Liver Diseases - Targeted Diagnosis and Therapy Using Specific Receptors and Ligands., editor. Wu GY and Wu CH, editors. Mariel Decker, Inc. Farmington; 1991. pp. 189–213. - PubMed
-
- McCashland TM, Tuma DJ, Sorrell MF, Casey CA. Zonal differences in ethanol-induced impairments in hepatic receptor binding. Alcohol. 1993;10:549–554. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

