Interferon and alternative activation of monocyte/macrophages in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 21425123
- PMCID: PMC4030759
- DOI: 10.1002/art.30318
Interferon and alternative activation of monocyte/macrophages in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
Objective: To explore the relationship between biomarkers of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), interferon (IFN)-regulated gene expression, and the alternative activation pathway in systemic sclerosis (SSc).
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were purified from healthy controls, patients with idiopathic PAH, and SSc patients (classified as having diffuse cutaneous SSc, limited cutaneous SSc [lcSSc] without PAH, and lcSSc with PAH). IFN-regulated and "PAH biomarker" genes were compared after supervised hierarchical clustering. Messenger RNA levels of selected IFN-regulated genes (Siglec1 and MX1), biomarker genes (IL13RA1, CCR1, and JAK2), and the alternative activation marker gene (MRC1) were analyzed on PBMCs and on CD14- and CD14+ cell populations. Interleukin-13 (IL-13) and IL-4 concentrations were measured in plasma by immunoassay. CD14, MRC1, and IL13RA1 surface expression was analyzed by flow cytometry.
Results: Increased PBMC expression of both IFN-regulated and biomarker genes distinguished SSc patients from healthy controls. Expression of genes in the biomarker cluster, but not in the IFN-regulated cluster, distinguished lcSSc with PAH from lcSSc without PAH. The genes CCR1 (P<0.001) and JAK2 (P<0.001) were expressed more highly in lcSSc patients with PAH compared with controls and mainly by CD14+ cells. MRC1 expression was increased exclusively in lcSSc patients with PAH (P<0.001) and correlated strongly with pulmonary artery pressure (r=0.52, P=0.03) and higher mortality (P=0.02). MRC1 expression was higher in CD14+ cells and was greatly increased by stimulation with IL-13. IL-13 concentrations in plasma were most highly increased in lcSSc patients with PAH (P<0.001).
Conclusion: IFN-regulated and biomarker genes represent distinct, although related, clusters in lcSSc patients with PAH. MRC1, a marker for the effect of IL-13 on alternative monocyte/macrophage activation, is associated with this severe complication and is related to mortality.
Copyright © 2011 by the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures


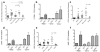
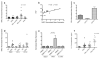

References
-
- Steen V, Medsger TA., Jr Predictors of isolated pulmonary hypertension in patients with systemic sclerosis and limited cutaneous involvement. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:516–22. - PubMed
-
- Wells AU, Steen V, Valentini G. Pulmonary complications: one of the most challenging complications of systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009;48(Suppl 3):iii40–4. - PubMed
-
- York MR, Nagai T, Mangini AJ, Lemaire R, van Seventer JM, Lafyatis R. A macrophage marker, Siglec-1, is increased on circulating monocytes in patients with systemic sclerosis and induced by type I interferons and Toll-like receptor agonists. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1010–20. - PubMed
-
- Clements P, Lachenbruch P, Seibold J, White B, Weiner S, Martin R, et al. Inter and intraobserver variability of total skin thickness score (modified Rodnan TSS) in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 1995;22:1281–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

