Interleukin-2/interleukin-2 antibody therapy induces target organ natural killer cells that inhibit central nervous system inflammation
- PMID: 21425186
- PMCID: PMC3082615
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.22339
Interleukin-2/interleukin-2 antibody therapy induces target organ natural killer cells that inhibit central nervous system inflammation
Abstract
Objective: The role of natural killer (NK) cells in regulating multiple sclerosis (MS) is not well understood. Additional studies with NK cells might provide insight into the mechanism of action of MS therapies such as daclizumab, an antibody against the interleukin (IL)-2R α-chain, which induces expansion of CD56(bright) NK cells.
Methods: In a relapsing-remitting form of the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of MS induced in SJL mice, we expanded NK cells with IL-2 coupled with an anti-IL-2 monoclonal antibody (mAb) and evaluated the effects of these NK cells on EAE. Further, we investigated the effect of the human version of IL-2/IL-2 mAb on NK cells from MS patients and its effect on central nervous system (CNS) inflammation and pathology in a human-mouse chimera model and assessed the underlying mechanisms.
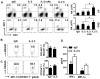
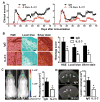
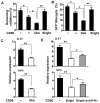
Results: IL-2/IL-2 mAb dramatically expands NK cells both in the peripheral lymphoid organs and in the CNS, and attenuates CNS inflammation and neurological deficits. Disease protection is conferred by CNS-resident NK cells. Importantly, the human version of IL-2/IL-2 mAb restored the defective CD56(+) NK cells from MS patients in a human-mouse chimera model. Both the CD56(bright) and CD56(dim) subpopulations were required to attenuate disease in this model.
Interpretation: These findings unveil the immunotherapeutic potential of NK cells, which can act as critical suppressor cells in target organs of autoimmunity. These results also have implications to better understand the mechanism of action of daclizumab in MS.
Copyright © 2011 American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
D. Campagnolo is an employee and stock holder of Biogen Idec. Inc. T. Vollmer received research grants and honoraria from Biogen Idec. Inc. and was involved in clinical trials of daclizumab.
Figures




Comment in
-
Comment on "Interleukin-2/interleukin-2 antibody therapy induces target organ natural killer cells that inhibit central nervous system inflammation".Ann Neurol. 2012 Jan;71(1):148-9. doi: 10.1002/ana.22547. Ann Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22275261 No abstract available.
References
-
- Li Z, Lim WK, Mahesh SP, et al. Cutting edge: in vivo blockade of human IL-2 receptor induces expansion of CD56(bright) regulatory NK cells in patients with active uveitis. J Immunol. 2005;174:5187–5191. - PubMed
-
- Wynn D, Kaufman M, Montalban X, et al. Daclizumab in active relapsing multiple sclerosis (CHOICE study): a phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, add-on trial with interferon beta. Lancet neurology. 2010;9:381–390. - PubMed
-
- Rose JW, Watt HE, White AT, Carlson NG. Treatment of multiple sclerosis with an anti-interleukin-2 receptor monoclonal antibody. Annals of neurology. 2004;56:864–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

