Systemic lupus erythematosus and cardiovascular disease: prediction and potential for therapeutic intervention
- PMID: 21426260
- PMCID: PMC3718673
- DOI: 10.1586/eci.10.98
Systemic lupus erythematosus and cardiovascular disease: prediction and potential for therapeutic intervention
Abstract
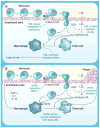
Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus have a significantly increased risk of cardiovascular events due to atherosclerosis. Traditional cardiac risk factors cannot fully explain this increased risk. Recent evidence strongly suggests that atherosclerotic plaque is largely driven by inflammation and an active immunological response, in contrast to the long-held belief that plaque is a passive accumulation of lipids in the arterial wall. Current approaches to the prevention of atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus involve targeting modifiable cardiac risk factors. Future preventive strategies may include therapies that counteract the immunologic responses that lead to plaque formation.
Figures
References
-
- Urowitz MB, Bookman AA, Koehler BE, Gordon DA, Smythe HA, Ogryzlo MA. The bimodal mortality pattern of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1976;60(2):221–225. - PubMed
-
- Manzi S, Meilahn EN, Rairie JE, et al. Age-specific incidence rates of myocardial infarction and angina in women with systemic lupus erythematosus: comparison with the Framingham Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1997;145(5):408–415. - PubMed
-
- Gladman DD, Urowitz MB. Morbidity in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1987;14(Suppl. 13):S223–S226. - PubMed
-
- Petri M, Perez-Gutthann S, Spence D, Hochberg MC. Risk factors for coronary artery disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1992;93(5):513–519. - PubMed
-
- Jonsson H, Nived O, Sturfelt G. Outcome in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective study of patients from a defined population. Medicine (Baltimore) 1989;68(3):141–150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
