Rice root-associated bacteria: insights into community structures across 10 cultivars
- PMID: 21426364
- PMCID: PMC4339037
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01092.x
Rice root-associated bacteria: insights into community structures across 10 cultivars
Abstract
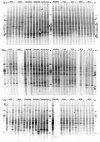
In this study, the effects of plant genotype, soil type and nutrient use efficiency on the composition of different bacterial communities associated with rice roots were investigated. Thus, total bacteria, Alpha- and Betaproteobacteria, Pseudomonas and Actinobacteria were studied using PCR, followed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (PCR-DGGE). Rice genotype determined, to a large extent, the composition of the different bacterial communities across cultivars. Several cultivars belonging to Oryza sativa ssp. indica tended to select similar bacterial communities, whereas those belonging to subspecies japonica and aromatica selected ones with divergent community structures. An effect of soil type was pronounced for the Actinobacteria communities, while a small effect of 'improved' and 'traditional' plants was noted for all communities analyzed. A few dominant bands in PCR-DGGE, affiliated with Rhizobium radiobacter, Dickeya zeae, Mycobacterium bolletii and with members of the Rhizobiales, Rhodospirillaceae and Paenibacillaceae, were spread across cultivars. In contrast, a majority of bands (e.g. affiliated with Enterobacter cloacae or Burkholderia kururiensis) was only present in particular cultivars or was erratically distributed among rice replicates. These findings suggested that both bacterial adaptation and plant genotype contribute to the shaping of the dynamic bacterial communities associated with roots of rice plants.
© 2011 Federation of European Microbiological Societies. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Andreote FD, Araújo WL, Azevedo JL, van Elsas JD, Nunes da Rocha U, van Overbeek LS. Endophytic colonization of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) by a novel competent bacterial endophyte, Pseudomonas putida strain P9, and its effect on associated bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009;75:3396–3406. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bais HP, Weir TL, Perry LG, Gilroy S, Vivanco JM. The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plant and other organisms. Annu Rev Plant Biology. 2006;57:233–266. - PubMed
-
- Biswas JC, Ladha JK, Dazzo FB, Yanni YG, Rolfe BG. Rhizobial inoculation influences seedling vigor and yield of rice. Agron J. 2000;92:880–886.
-
- Brandl MT. Fitness of human enteric pathogens on plants and implications for food safety. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2006;44:367–392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

