Divergent roles for the two PolI-like organelle DNA polymerases of Arabidopsis
- PMID: 21427281
- PMCID: PMC3091039
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.111.173849
Divergent roles for the two PolI-like organelle DNA polymerases of Arabidopsis
Abstract
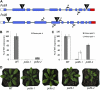
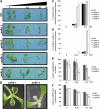
DNA polymerases play a central role in the process of DNA replication. Yet, the proteins in charge of the replication of plant organelle DNA have not been unambiguously identified. There are however many indications that a family of proteins homologous to bacterial DNA polymerase I (PolI) is implicated in organelle DNA replication. Here, we have isolated mutant lines of the PolIA and PolIB genes of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) to test this hypothesis. We find that mutation of both genes is lethal, thus confirming an essential and redundant role for these two proteins. However, the mutation of a single gene is sufficient to cause a reduction in the levels of DNA in both mitochondria and plastids. We also demonstrate that polIb, but not polIa mutant lines, are hypersensitive to ciprofloxacin, a small molecule that specifically induces DNA double-strand breaks in plant organelles, suggesting a function for PolIB in DNA repair. In agreement with this result, a cross between polIb and a plastid Whirly mutant line yielded plants with high levels of DNA rearrangements and severe growth defects, indicating impairments in plastid DNA repair pathways. Taken together, this work provides further evidences for the involvement of the plant PolI-like genes in organelle DNA replication and suggests an additional role for PolIB in DNA repair.
Figures


References
-
- Bendich AJ. (2007) The size and form of chromosomes are constant in the nucleus, but highly variable in bacteria, mitochondria and chloroplasts. Bioessays 29: 474–483 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

