Vav guanine nucleotide exchange factors link hyperlipidemia and a prothrombotic state
- PMID: 21427288
- PMCID: PMC3110031
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-01-201970
Vav guanine nucleotide exchange factors link hyperlipidemia and a prothrombotic state
Abstract
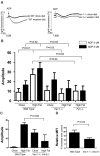
Platelet hyperactivity associated with hyperlipidemia contributes to development of a pro-thrombotic state. We previously showed that oxidized LDL (oxLDL) formed in the setting of hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis initiated a CD36-mediated signaling cascade leading to platelet hyperactivity. We now show that the guanine nucleotide exchange factors Vav1 and Vav3 were tyrosine phosphorylated in platelets exposed to oxLDL. Pharmacologic inhibition of src family kinases abolished Vav1 phosphorylation by oxLDL in vitro. Coimmunoprecipitations revealed the tyrosine phosphorylated form of src kinase Fyn was associated with Vav1 in platelets exposed to oxLDL. Using a platelet aggregation assay, we demonstrated that Vav1 deficiency, Fyn deficiency, or Vav1/Vav3 deficiency protected mice from diet-induced platelet hyperactivity. Furthermore, flow cytometric analysis revealed that Vav1/Vav3 deficiency significantly inhibited oxLDL-mediated integrin αIIbβIII activation of platelets costimulated with ADP. Finally, we showed with an in vivo carotid artery thrombosis model that genetic deletion of Vav1 and Vav3 together may prevent the development of occlusive thrombi in mice fed a high-fat diet. These findings implicate Vav proteins in oxLDL-mediated platelet activation and suggest that Vav family member(s) may act as critical modulators linking a prothrombotic state and hyperlipidemia.
Figures


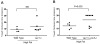
Comment in
-
Vav-Vav-Vav-voom!Blood. 2011 May 26;117(21):5557-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-04-345561. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21617008 No abstract available.
References
-
- Podrez EA, Poliakov E, Shen Z, et al. Identification of a novel family of oxidized phospholipids that serve as ligands for the macrophage scavenger receptor CD36. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(41):38503–38516. - PubMed
-
- Podrez EA, Poliakov E, Shen Z, et al. A novel family of atherogenic oxidized phospholipids promotes macrophage foam cell formation via the scavenger receptor CD36 and is enriched in atherosclerotic lesions. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(41):38517–38523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

