The effects of maribavir on the autophosphorylation of ganciclovir resistant mutants of the cytomegalovirus UL97 protein
- PMID: 21429239
- PMCID: PMC3050433
- DOI: 10.1186/2042-4280-1-4
The effects of maribavir on the autophosphorylation of ganciclovir resistant mutants of the cytomegalovirus UL97 protein
Abstract
Background: The UL97 protein kinase of human cytomegalovirus phosphorylates the antiviral drug ganciclovir and is the target of maribavir action. A detailed enzyme kinetic analysis of maribavir on the various enzymatic functions of wild type and ganciclovir resistant forms of UL97 is required.
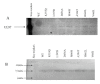
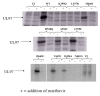
Methods: Wild type and site directed mutant forms of the human cytomegalovirus UL97 gene product were expressed using recombinant baculoviruses and the purified products used to assess the effects of maribavir on the ganciclovir (GCV) kinase and protein kinase (PK) activities.
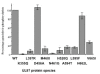
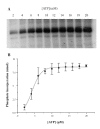
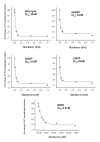
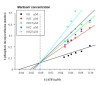
Results: Maribavir was a potent inhibitor of the autophosporylation of the wild type and all the major GCV resistant UL97 mutants analysed (M460I, H520Q, A594V and L595F) with a mean IC50 of 35 nM. The M460I mutation resulted in hypersensitivity to maribavir with an IC50 of 4.8 nM. A maribavir resistant mutant of UL97 (L397R) was functionally compromised as both a GCV kinase and a protein kinase (~ 10% of wild type levels). Enzyme kinetic experiments demonstrated that maribavir was a competitive inhibitor of ATP with a Ki of 10 nM.
Discussion: Maribavir is a potent competitive inhibitor of the UL97 protein kinase function and shows increased activity against the M460I GCV-resistant mutant which may impact on the management of GCV drug resistance in patients.
Figures

References
-
- Michel D, Schaarschmidt P, Wunderlich K, Heuschmid M, Simoncini L, Mühlberger D, Zimmermann A, Pavić I, Mertens T. Functional regions of the human cytomegalovirus protein pUL97 involved in nuclear localization and phosphorylation of ganciclovir and pUL97 itself. J Gen Virol. 1998;79(Pt 9):2105–12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

