Long term antipsychotic treatment does not alter metabolite concentrations in rat striatum: an in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy study
- PMID: 21429713
- PMCID: PMC3085587
- DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2011.02.019
Long term antipsychotic treatment does not alter metabolite concentrations in rat striatum: an in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy study
Abstract
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) studies of schizophrenic patients generally reveal reduced levels of N-acetyl aspartate (NAA) when compared with healthy controls. Whether this reduction is due to the disease or to the drugs used for treatment remains an open question. Numerous human and animal studies have attempted to determine the effects of antipsychotics on NAA levels with mixed results. The majority of the animal studies were ex vivo, which may not accurately reflect the in vivo situation, and limitations of the human studies include previous or concomitant medications or other confounds. To overcome these limitations, we dosed 10 rats/group for six months via drinking water with 0.2 or 2 mg/kg/day haloperidol or 10 or 30 mg/kg/day clozapine. Control rats received unadulterated water. Proton MRS data were collected longitudinally over the six month period from a 64 μL voxel containing primarily the right striatum prior to and monthly during drug administration and used to estimate the concentrations of NAA, creatine, and choline. Ratios of NAA, choline, inositol and glutamate+glutamine to creatine were also calculated. Only the Cho/Cr ratio showed a significant time-by-treatment effect (p=0.0285). These results are in agreement with previous studies of the striatum. However, regional and disease-specific effects remain unresolved.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
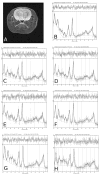
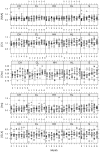
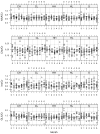
Similar articles
-
Effects of antipsychotic drugs on metabolite ratios in rat brain in vivo.Magn Reson Med. 2000 Mar;43(3):355-8. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1522-2594(200003)43:3<355::aid-mrm6>3.0.co;2-r. Magn Reson Med. 2000. PMID: 10725877
-
Long-term treatment of rats with haloperidol: lack of an effect on brain N-acetyl aspartate levels.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 Apr;31(4):751-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300874. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006. PMID: 16132064
-
Increased N-acetylaspartate in rat striatum following long-term administration of haloperidol.Schizophr Res. 2005 Jun 15;75(2-3):303-8. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2004.11.001. Epub 2004 Dec 1. Schizophr Res. 2005. PMID: 15885521
-
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy as a probe into the pathophysiology of autism spectrum disorders (ASD): a review.Autism Res. 2013 Apr;6(2):119-33. doi: 10.1002/aur.1273. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Autism Res. 2013. PMID: 23436782 Review.
-
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the human brain in schizophrenia.Rev Neurosci. 2000;11(2-3):147-58. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2000.11.2-3.147. Rev Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10718151 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Antipsychotic Administration on Brain Glutamate in Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review of Longitudinal 1H-MRS Studies.Front Psychiatry. 2017 Apr 28;8:66. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00066. eCollection 2017. Front Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28503156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of atypical antipsychotics on brain N-acetylaspartate levels in antipsychotic-naïve first-episode patients with schizophrenia: a preliminary study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014 Jul 7;10:1243-53. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S61415. eCollection 2014. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014. PMID: 25045268 Free PMC article.
-
Decoupling of N-acetyl-aspartate and glutamate within the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia.Curr Mol Med. 2015;15(2):176-83. doi: 10.2174/1566524015666150303104811. Curr Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25732147 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related changes in anterior cingulate cortex glutamate in schizophrenia: A (1)H MRS Study at 7 Tesla.Schizophr Res. 2016 Apr;172(1-3):101-5. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2016.02.017. Epub 2016 Feb 28. Schizophr Res. 2016. PMID: 26925800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Assis LC, Scaini G, Di-Pietro PB, Castro AA, Comim CM, Streck EL, Quevedo J. Effect of antipsychotics on creatine kinase activity in rat brain. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;101(5):315–319. - PubMed
-
- Bartzokis G, Lu PH, Stewart SB, Oluwadara B, Lucas AJ, Pantages J, Pratt E, Sherin JE, Altshuler LL, Mintz J, Gitlin MJ, Subotnik KL, Nuechterlein KH. In vivo evidence of differential impact of typical and atypical antipsychotics on intracortical myelin in adults with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2009;113(2–3):322–331. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertolino A, Callicott JH, Mattay VS, Weidenhammer KM, Rakow R, Egan MF, Weinberger DR. The effect of treatment with antipsychotic drugs on brain N-acetylaspartate measures in patients with schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2001;49(1):39–46. - PubMed
-
- Brugger S, Davis JM, Leucht S, Stone JM. Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Illness Stage in Schizophrenia-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biol Psychiatry 2010 - PubMed
-
- Bustillo J, Barrow R, Paz R, Tang J, Seraji-Bozorgzad N, Moore GJ, Bolognani F, Lauriello J, Perrone-Bizzozero N, Galloway MP. Long-term treatment of rats with haloperidol: lack of an effect on brain N-acetyl aspartate levels. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31(4):751–756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

