Fatal mycotic aneurysms due to Scedosporium and Pseudallescheria infection
- PMID: 21430108
- PMCID: PMC3122655
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02615-10
Fatal mycotic aneurysms due to Scedosporium and Pseudallescheria infection
Abstract
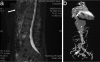
Angioinvasive complications of Scedosporium infections are rare. We report two cases of mycotic aneurysm, following apparent localized infection, due to Scedosporium apiospermum and Pseudallescheria boydii. The thoracoabdominal aorta was affected in one patient, and cerebral vessels were affected in the other. Despite voriconazole therapy and surgical resection, the patients died. Previously reported cases are reviewed.
Figures

References
-
- Ahsan H., Ajmal F., Saleem M. F., Sonawala A. B. 2009. Cerebral fungal infection with mycotic aneurysm of basilar artery and subarachnoid haemorrhage. Singapore Med. J. 50:e22–e25 - PubMed
-
- Baudrillard J. C., et al. 1985. Fungal mycotic aneurysms and multiple cerebral abscesses caused by Scedosporium apiospermum. Apropos of a case with review of the literature. J. Radiol. 66:321–326 - PubMed
-
- Ben Hamida M., et al. 1993. Fungal mycotic aneurysms and visceral infection due to Scedosporium apiospermum in a kidney transplant patient. Transplant Proc. 25:2290–2291 - PubMed
-
- Castiglioni B., Sutton D. A., Rinaldi M. G., Fung J., Kusne S. 2002. Pseudallescheria boydii (anamorph Scedosporium apiospermum). Infection in solid organ transplant recipients in a tertiary medical center and review of the literature. Medicine 81:333–348 - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2008. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of filamentous fungi, 2nd ed. Approved standard M38-A2. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

