The importance of being variable
- PMID: 21430150
- PMCID: PMC3104038
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5641-10.2011
The importance of being variable
Abstract
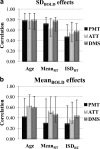
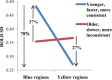
New work suggests that blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) signal variability can be a much more powerful index of human age than mean activation, and that older brains are actually less variable than younger brains. However, little is known of how BOLD variability and task performance may relate. In the current study, we examined BOLD variability in relation to age, and reaction time speed and consistency in healthy younger (20-30 years) and older (56-85 years) adults on three cognitive tasks (perceptual matching, attentional cueing, and delayed match-to-sample). Results indicated that younger, faster, and more consistent performers exhibited significantly higher brain variability across tasks, and showed greater variability-based regional differentiation compared with older, poorer-performing adults. Also, when we compared brain variability- and typical mean-based effects, the respective spatial patterns were essentially orthogonal across brain measures, and any regions that did overlap were largely opposite in directionality of effect. These findings help establish the functional basis of BOLD variability, and further support the statistical and spatial differentiation between BOLD variability and BOLD mean. We thus argue that the precise nature of relations between aging, cognition, and brain function is underappreciated by using mean-based brain measures exclusively.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Baltes PB, Lindenberger U. Emergence of a powerful connection between sensory and cognitive functions across the adult life span: a new window to the study of cognitive aging? Psychol Aging. 1997;12:12–21. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann CF, Smith SM. Probabilistic independent component analysis for functional magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2004;23:137–152. - PubMed
-
- Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1995;34:537–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
