Anterior hippocampus and goal-directed spatial decision making
- PMID: 21430161
- PMCID: PMC6622909
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4640-10.2011
Anterior hippocampus and goal-directed spatial decision making
Abstract
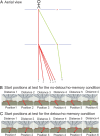
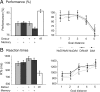
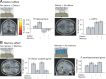
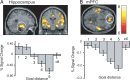
Planning spatial paths through our environment is an important part of everyday life and is supported by a neural system including the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Here we investigated the precise functional roles of the components of this system in humans by using fMRI as participants performed a simple goal-directed route-planning task. Participants had to choose the shorter of two routes to a goal in a visual scene that might contain a barrier blocking the most direct route, requiring a detour, or might be obscured by a curtain, requiring memory for the scene. The participant's start position was varied to parametrically manipulate their proximity to the goal and the difference in length of the two routes. Activity in medial prefrontal cortex, precuneus, and left posterior parietal cortex was associated with detour planning, regardless of difficulty, whereas activity in parahippocampal gyrus was associated with remembering the spatial layout of the visual scene. Activity in bilateral anterior hippocampal formation showed a strong increase the closer the start position was to the goal, together with medial prefrontal, medial and posterior parietal cortices. Our results are consistent with computational models in which goal proximity is used to guide subsequent navigation and with the association of anterior hippocampal areas with nonspatial functions such as arousal and reward expectancy. They illustrate how spatial and nonspatial functions combine within the anterior hippocampus, and how these functions interact with parahippocampal, parietal, and prefrontal areas in decision making and mnemonic function.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Posterior-Anterior Distinction between Scene Perception and Scene Construction in Human Medial Parietal Cortex.J Neurosci. 2019 Jan 23;39(4):705-717. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1219-18.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 30. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30504281 Free PMC article.
-
A temporoparietal and prefrontal network for retrieving the spatial context of lifelike events.Neuroimage. 2001 Aug;14(2):439-53. doi: 10.1006/nimg.2001.0806. Neuroimage. 2001. PMID: 11467917
-
Synchronization of medial temporal lobe and prefrontal rhythms in human decision making.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 9;33(2):442-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2573-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23303925 Free PMC article.
-
Parietal and hippocampal contribution to topokinetic and topographic memory.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1997 Oct 29;352(1360):1437-48. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1997.0130. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1997. PMID: 9368932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial navigation and hippocampal place cell firing: the problem of goal encoding.Rev Neurosci. 2004;15(2):89-107. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2004.15.2.89. Rev Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15202682 Review.
Cited by
-
Neural basis of topographical disorientation in the primate posterior cingulate gyrus based on a labeled graph.AIMS Neurosci. 2022 Sep 9;9(3):373-394. doi: 10.3934/Neuroscience.2022021. eCollection 2022. AIMS Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36329903 Free PMC article.
-
Scale-Free Navigational Planning by Neuronal Traveling Waves.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 9;10(7):e0127269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127269. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26158660 Free PMC article.
-
Phase-tuned neuronal firing encodes human contextual representations for navigational goals.Elife. 2018 Jun 22;7:e32554. doi: 10.7554/eLife.32554. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29932417 Free PMC article.
-
Dissociable representations of environmental size and complexity in the human hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2013 Jun 19;33(25):10526-33. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0350-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23785164 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Mechanisms of Hierarchical Planning in a Virtual Subway Network.Neuron. 2016 May 18;90(4):893-903. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.03.037. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 27196978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adcock RA, Thangavel A, Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Knutson B, Gabrieli JD. Reward-motivated learning: mesolimbic activation precedes memory formation. Neuron. 2006;50:507–517. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre GK, Detre JA, Alsop DC, D'Esposito M. The parahippocampus subserves topographical learning in man. Cereb Cortex. 1996;6:823–829. - PubMed
-
- Andersen RA, Essick GK, Seigel RM. Encoding of spatial location by posterior parietal neurons. Science. 1985;230:456–458. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman DM, Rawlins JN, McHugh SB, Deacon RM, Yee BK, Bast T, Zhang WN, Pothuizen HH, Feldon J. Regional dissociations within the hippocampus-memory and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004;28:273–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
