Alteration of hepatic but not renal transporter expression in diet-induced obese mice
- PMID: 21430232
- PMCID: PMC3100907
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.110.037507
Alteration of hepatic but not renal transporter expression in diet-induced obese mice
Abstract
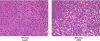
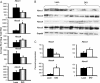
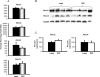
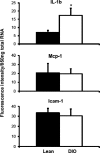
Drug pharmacokinetics can be altered in obese and diabetic subjects. In consideration of the prevalence of obesity and diabetes, characterization of transporter expression in mouse models of diabetes and obesity may be a useful tool to aid in prediction of altered drug pharmacokinetics or adverse drug reactions. It has been reported that ob/ob mice, which display a severe obesity and diabetes phenotype, exhibit multiple changes in drug transporter expression in liver and kidney. In the present study, the mRNA and protein expression of major drug transporters was determined in livers and kidneys of diet-induced obese (DIO) C57BL/6J male mice. The mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD) (60% fat) from 6 weeks of age and display obesity, fatty liver, and mild hyperglycemia. The HFD diet increased expression of multidrug resistance-associated proteins Abcc3 and 4 mRNA and protein in liver by 3.4- and 1.4-fold, respectively, compared with that detected in control mice fed a low-fat diet (LFD). In contrast, Abcc1 mRNA and protein decreased by 50% in livers of DIO mice compared with those in livers to lean mice. The HFD did not alter transporter expression in kidney compared with the LFD. In summary, unlike ob/ob and db/db mice, DIO mice exhibited a selective induction of efflux transporter expression in liver (i.e., Abcc3 and 4). In addition, diet-induced obesity affects transporter expression in liver but not kidney in the C57BL/6J mouse model. These data indicate that hepatic transporter expression is only slightly altered in a model of mild diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity.
Figures

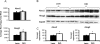
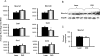

References
-
- Aleksunes LM, Slitt AM, Cherrington NJ, Thibodeau MS, Klaassen CD, Manautou JE. (2005) Differential expression of mouse hepatic transporter genes in response to acetaminophen and carbon tetrachloride. Toxicol Sci 83:44–52 - PubMed
-
- Bergman SJ, Speil C, Short M, Koirala J. (2007) Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic aspects of antibiotic use in high-risk populations. Infect Dis Clin North Am 21:821–846, x - PubMed
-
- Buist SC, Klaassen CD. (2004) Rat and mouse differences in gender-predominant expression of organic anion transporter (Oat1–3; Slc22a6–8) mRNA levels. Drug Metab Dispos 32:620–625 - PubMed
-
- Bush EN, Shapiro R, Nuss M, Kaszubska W, Trevillyan J, Knourek-Segel V, Kennedy M, Adler A, Jirousek M, Jacobson P. (2001) Adiposity, leptin resistance, hyperrphagia, hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance and insulin resistance in C57BL/6J mice fed high fat diets, in Proceedings of the 83rd Annual Meeting and Expo of the Endocrine Society; 2001 Jun 20–23; Denver, CO The Endocrine Society, Chevy Chase, MD
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

