Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors
- PMID: 21430269
- PMCID: PMC3132801
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002003
Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors
Abstract
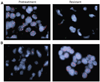
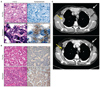
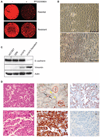
Lung cancers harboring mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) respond to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, but drug resistance invariably emerges. To elucidate mechanisms of acquired drug resistance, we performed systematic genetic and histological analyses of tumor biopsies from 37 patients with drug-resistant non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) carrying EGFR mutations. All drug-resistant tumors retained their original activating EGFR mutations, and some acquired known mechanisms of resistance including the EGFR T790M mutation or MET gene amplification. Some resistant cancers showed unexpected genetic changes including EGFR amplification and mutations in the PIK3CA gene, whereas others underwent a pronounced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Surprisingly, five resistant tumors (14%) transformed from NSCLC into small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and were sensitive to standard SCLC treatments. In three patients, serial biopsies revealed that genetic mechanisms of resistance were lost in the absence of the continued selective pressure of EGFR inhibitor treatment, and such cancers were sensitive to a second round of treatment with EGFR inhibitors. Collectively, these results deepen our understanding of resistance to EGFR inhibitors and underscore the importance of repeatedly assessing cancers throughout the course of the disease.
Figures
Comment in
-
Resisting targeted therapy: fifty ways to leave your EGFR.Cancer Cell. 2011 Apr 12;19(4):437-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.03.020. Cancer Cell. 2011. PMID: 21481786
-
Targeted therapies: evolve and ... surrender!Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011 Jun;8(6):315. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.60. Epub 2011 May 3. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21544054 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, Louis DN, Christiani DC, Settleman J, Haber DA. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, Naoki K, Sasaki H, Fujii Y, Eck MJ, Sellers WR, Johnson BE, Meyerson M. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J, Politi K, Sarkaria I, Singh B, Heelan R, Rusch V, Fulton L, Mardis E, Kupfer D, Wilson R, Kris M, Varmus H. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2004;101:13306–13311. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, Nishiwaki Y, Ohe Y, Yang JJ, Chewaskulyong B, Jiang H, Duffield EL, Watkins CL, Armour AA, Fukuoka M. Gefitinib or carboplatin–paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009;361:947–957. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Moran T, Queralt C, Porta R, Cardenal F, Camps C, Majem M, Lopez-Vivanco G, Isla D, Provencio M, Insa A, Massuti B, Gonzalez-Larriba JL, Paz-Ares L, Bover I, Garcia-Campelo R, Moreno MA, Catot S, Rolfo C, Reguart N, Palmero R, Sánchez JM, Bastus R, Mayo C, Bertran-Alamillo J, Molina MA, Sanchez JJ, Taron M. Spanish Lung Cancer Group, Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009;361:958–967. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P20 CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01CA141457-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA120060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140594/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 GRANT CA120060-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA127003/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA140594/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA137008/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA141457/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA137008-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA156000/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

