Optimal cutoff point for immunoperoxidase detection of C4d in the renal allograft: results from a multicenter study
- PMID: 21430605
- PMCID: PMC3171966
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181f7fec9
Optimal cutoff point for immunoperoxidase detection of C4d in the renal allograft: results from a multicenter study
Abstract
Background: Although C4d deposition in peritubular capillaries has been identified as a strong risk factor for subsequent renal allograft loss, the optimal cutoff for the fraction of peritubular capillaries needed to establish a positive stain in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded material has not been defined systematically. The objective of this study was to establish the threshold for positive staining that best predicts renal outcome in renal biopsies in a multicenter study in which local and central pathologic conditions were compared.
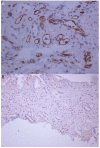
Methods: Unstained renal biopsy slides were obtained from 296 patients. The percentage of peritubular capillaries staining positively for C4d was detected by immunoperoxidase staining.
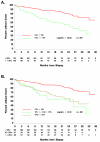
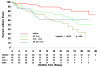
Results: The percentage C4d deposition ranged from 0% to 90% with 44% (129/296) having a positive percentage of C4d staining. The median for positive cases was 25%. Local C4d+ results were reported qualitatively, with 28% recorded as positive for C4d. Using a centrally determined cutoff of 10%, tests for agreement of local and central C4d staining were fair (κ 0.40, 95% confidence interval 0.29-0.51). Raising the centrally determined cutoff to 25% or 50% did not change the κ values (0.44 and 0.41, respectively). By Cox proportional hazards model, C4d positivity (centrally determined assessment) using a cutoff of 10% was the strongest predictor of time to graft loss (hazard ratio 2.66, 95% confidence interval 1.68-4.21). Centrally determined C4d positivity correlated with Banff scores indicative of acute inflammation but not with scores indicative of fibrosis/atrophy or transplant glomerulopathy.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that C4d positivity, defined as more than or equal to 10% by immunoperoxidase, is a strong predictor of graft loss.
Figures
References
-
- Feucht HE, Mihatsch MJ. Diagnostic value of C4d in renal biopsies. Current Opinion in Nephrology & Hypertension. 2005;14(6):592. - PubMed
-
- Wang R, Wang H, Chen J, et al. C4d deposition in allograft renal biopsies is an independent risk factor for graft failure. Nephrology. 2009;14(5):527. - PubMed
-
- Herzenberg AM, Gill JS, Djurdjev O, Magil AB. C4d deposition in acute rejection: an independent long-term prognostic factor. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2002;13(1):234. - PubMed
-
- Racusen LC, Colvin RB, Solez K, et al. Antibody-mediated rejection criteria - an addition to the Banff 97 classification of renal allograft rejection. American Journal of Transplantation. 2003;3(6):708. - PubMed
-
- Mauiyyedi S, Pelle PD, Saidman S, et al. Chronic humoral rejection: identification of antibody-mediated chronic renal allograft rejection by C4d deposits in peritubular capillaries. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12(3):574. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

