Status of disulfiram in present day alcoholic deaddiction therapy
- PMID: 21431004
- PMCID: PMC3056183
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5545.75557
Status of disulfiram in present day alcoholic deaddiction therapy
Abstract
Aim: Assessment of safety and efficacy profile of disulfiram (DSM) in the alcoholic de-addiction regimen.
Objectives: a. Assessment of Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) profile; b. Evaluation of effectiveness of various deaddiction regimen; c. Defaulters and dropouts
Patients and methods: Fifty-one patients in a de-addiction center were investigated on 0(th) , 30(th) and 60(th) day along with psychiatric evaluation, ADR surveillance was made. Statistical analysis was done thereafter.
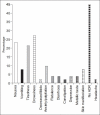
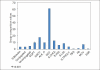
Results: 125 mg DSM given OD for 2 months. 76.5% patients had taken full course of treatment, 45% didn't complain of any ADR. Of ADR reported 27.4% had drowsiness, 21.4% tiredness, 7.8% skin manifestation.
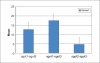
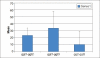
Conclusion: DSM is the main drug among naltrexone, acamprosate, nalmefene and other drugs used in alcoholic de-addiction. Relative and effectiveness is lost by the degree of dropouts and hence relapses. Low-dose DSM had decreased adverse effects with 76.5% patients taking the full course of treatment. DSM alters liver functions as there were significant changes in the lab parameters of SGPT(P=0.007), SGOT(P=0.001), GGT(P=<0.001) between first and third samples. Occurrence of ADR is not the cause of default; patients find it confusing to differentiate between the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal and those due to ADR of DSM.
Keywords: Adverse drug reaction; alcohol de-addiction; de-addiction regimen; disulfiram; drug default.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- De Souza Avinash. Studies of family supervised disulfiram, naltrexone and acamprosate in the Indian setting. 2006. Proceedings of 3rd Berlin Stapleford International Addiction Conference on latest developments in effective medical treatments for addiction; Berlin March 18 - 19th avinashdes999@yahoo.com .
-
- Christensen JK, Rønsted P, Vaag UH. Side effects after disulfiram: Comparison of disulfiram and placebo in a double-blind multicentre study. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1984;69:265–73. - PubMed
-
- Borup C, Kaiser A, Jenson E. Long term antabuse treatment: Tolerance and reasons for withdrawal. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1992;369:47–9. - PubMed
-
- Enghusen Poulsen H, Loft S, Andersen JR, Andersen M. Disulfiram therapy--adverse drug reactions and interactions. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1992;369:59–65. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

