Effect of habitual exercise on renal carcinogenesis by ferric nitrilotriacetate
- PMID: 21431792
- PMCID: PMC3117213
- DOI: 10.1007/s12199-010-0191-9
Effect of habitual exercise on renal carcinogenesis by ferric nitrilotriacetate
Abstract
Objectives: We investigated whether habitual exercise (HE) (treadmill running) suppresses development of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) induced by ferric nitrilotriacetate (Fe-NTA).
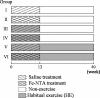
Methods: Male Fischer 344 rats were divided into six groups: group I, saline treatment (12 weeks = initiation period) and non-HE; group II, Fe-NTA treatment (12 weeks) and non-HE; group III, saline treatment and short-term (12 weeks) HE; group IV, Fe-NTA treatment and short-term HE; group V, saline treatment and long-term (40 weeks) HE; and group VI, Fe-NTA treatment and long-term HE. Saline treatment groups did not develop RCC, therefore we investigated the effects of HE among Fe-NTA treatment groups.
Results: Gross nodules (diagnosed as RCC), RCC represented by microcarcinomas (Mcs), karyomegalic cells (KCs), and degenerative tubules (DTs) were seen in rats treated with Fe-NTA. The number of Mcs, KCs, and DTs were increased in the short-term HE group when compared with those in the non-HE group, but were decreased in the long-term HE group when compared with those in the short-term HE group.
Conclusions: Short-term (initiation period) HE promoted renal carcinogenesis induced by Fe-NTA; however, long-term HE after the initiation period suppressed the promoted carcinogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sex hormone-dependent renal cell carcinogenesis induced by ferric nitrilotriacetate in Wistar rats.Jpn J Cancer Res. 1995 Nov;86(11):1068-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1995.tb03022.x. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1995. PMID: 8567398 Free PMC article.
-
Consumption of hydrogen-rich water protects against ferric nitrilotriacetate-induced nephrotoxicity and early tumor promotional events in rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Nov;61:248-54. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.10.004. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 24140467
-
Renal carcinogenesis induced by ferric nitrilotriacetate in mice, and protection from it by Brazilian propolis and artepillin C.Pathol Int. 2000 Sep;50(9):679-89. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1827.2000.01097.x. Pathol Int. 2000. PMID: 11012980
-
Subacute nephrotoxicity and induction of renal cell carcinoma in mice treated with ferric nitrilotriacetate.Cancer Res. 1987 Apr 1;47(7):1867-9. Cancer Res. 1987. PMID: 3815378
-
The Role of Ferric Nitrilotriacetate in Renal Carcinogenesis and Cell Death: From Animal Models to Clinical Implications.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 15;14(6):1495. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061495. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326646 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term voluntary exercise, representing habitual exercise, lowers visceral fat and alters plasma amino acid levels in mice.Environ Health Prev Med. 2012 Jul;17(4):275-84. doi: 10.1007/s12199-011-0249-3. Epub 2011 Nov 4. Environ Health Prev Med. 2012. PMID: 22052204 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Mechanisms of Aerobic Exercise on Cancer Initiation, Progression, and Metastasis: A Critical Systematic Review of In Vivo Preclinical Data.Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 15;76(14):4032-50. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0887. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27381680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention, Health Promotion Physical activity and good nutrition: essential elements to prevent chronic diseases and obesity 2003. Nutr Clin Care. 2003;6:135–138. - PubMed
-
- Ikuyama T, Watanabe T, Minegishi Y, Osanai H. Effect of voluntary exercise on 3-methyl-4-dimethylaminoazobenzene-induced hepatomas in male Jc1:Wistar rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1993;204:211–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
