The unconscious pursuit of emotion regulation: implications for psychological health
- PMID: 21432692
- PMCID: PMC3268658
- DOI: 10.1080/02699931.2010.532606
The unconscious pursuit of emotion regulation: implications for psychological health
Abstract
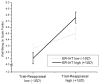
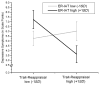
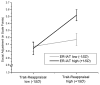
Because of the central involvement of emotion regulation in psychological health and the role that implicit (largely unconscious) processes appear to play in emotion regulation, implicit emotion-regulatory processes should play a vital role in psychological health. We hypothesised that implicitly valuing emotion regulation translates into better psychological health in individuals who use adaptive emotion-regulation strategies. A community sample of 222 individuals (56% women) who had recently experienced a stressful life event completed an implicit measure of emotion regulation valuing (ER-IAT) and reported on their habitual use of an important adaptive emotion-regulation strategy: cognitive reappraisal. We measured three domains of psychological health: well-being, depressive symptoms, and social adjustment. As hypothesised, individuals who implicitly valued emotion regulation exhibited greater levels of psychological health, but only when they were high in cognitive reappraisal use. These findings suggest that salutary effects of unconscious emotion-regulation processes depend on its interplay with conscious emotion-regulation processes.
© 2011 Psychology Press, an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an Informa business
Figures
Similar articles
-
Explicit and implicit emotion regulation: a dual-process framework.Cogn Emot. 2011 Apr;25(3):400-12. doi: 10.1080/02699931.2010.544160. Cogn Emot. 2011. PMID: 21432682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"I feel better but I don't know why": the psychology of implicit emotion regulation.Cogn Emot. 2011 Apr;25(3):389-99. doi: 10.1080/02699931.2010.550505. Cogn Emot. 2011. PMID: 21432681
-
Implicit loneliness, emotion regulation, and depressive symptoms in breast cancer survivors.J Behav Med. 2016 Oct;39(5):832-44. doi: 10.1007/s10865-016-9751-9. Epub 2016 Jun 10. J Behav Med. 2016. PMID: 27287618 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding reappraisal as a multicomponent process: The psychological health benefits of attempting to use reappraisal depend on reappraisal success.Emotion. 2017 Sep;17(6):905-911. doi: 10.1037/emo0000310. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Emotion. 2017. PMID: 28358559 Free PMC article.
-
Emotion Regulation Strategies in Depressive and Anxiety Symptoms in Youth: A Meta-Analytic Review.J Youth Adolesc. 2017 Feb;46(2):261-276. doi: 10.1007/s10964-016-0585-0. Epub 2016 Oct 12. J Youth Adolesc. 2017. PMID: 27734198 Review.
Cited by
-
The psychological resilience of teenagers in terms of their everyday emotional balance and the impact of emotion regulation strategies.Front Psychol. 2025 Feb 20;15:1381239. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1381239. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40052017 Free PMC article.
-
History of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy Is Associated with Increased Cognitive Reappraisal Ability.Mindfulness (N Y). 2013 Sep 1;4(3):213-222. doi: 10.1007/s12671-012-0114-5. Mindfulness (N Y). 2013. PMID: 26005504 Free PMC article.
-
Emotion regulation and mental health across cultures: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Nat Hum Behav. 2025 Jun;9(6):1176-1200. doi: 10.1038/s41562-025-02168-8. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Nat Hum Behav. 2025. PMID: 40234629
-
High cardiac vagal control protects against future depressive symptoms under conditions of high social support.Biol Psychol. 2013 Apr;93(1):143-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2013.01.004. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Biol Psychol. 2013. PMID: 23352570 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal course of implicit emotion regulation during a Priming-Identify task: an ERP study.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 2;7:41941. doi: 10.1038/srep41941. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28150801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bargh JA, Williams LE. The nonconscious regulation of emotion. In: Gross JJ, editor. Handbook of emotion regulation. New York, NY: Guilford Press; 2007. pp. 429–445.
-
- Baumann N, Kaschel R, Kuhl J. Striving for unwanted goals: Stress-dependent discrepancies between explicit and implicit achievement motives reduce subjective well-being and increase psychosomatic symptoms. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2005;89:781–799. - PubMed
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA. Internal consistencies of the original and revised Beck Depression Inventory. Journal of Clinical Psychology. 1984;40:1365–1367. - PubMed
-
- Bonanno GA. Loss, trauma, and human resilience: Have we underestimated the human capacity to thrive after extremely aversive events? American Psychologist. 2004;59:20–28. - PubMed
-
- Bonanno GA, Papa A, Lalande K, Westphal M, Coifman K. The importance of being flexible: The ability to both enhance and suppress emotional expression predicts long-term adjustment. Psychological Science. 2004;15:482–487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
