Beneficial cardiometabolic actions of telmisartan plus amlodipine therapy in elderly patients with poorly controlled hypertension
- PMID: 21432858
- PMCID: PMC6652664
- DOI: 10.1002/clc.20855
Beneficial cardiometabolic actions of telmisartan plus amlodipine therapy in elderly patients with poorly controlled hypertension
Abstract
Background: There is a growing body of evidence that blood pressure (BP) level is one of the major determinants of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in individuals, including elderly people. However, to achieve a target BP level in the elderly is more difficult compared with patients aged <65 years. Current guidelines recommend combination drug therapy with different modes of action for the treatment of elderly patients with moderate hypertension (HT). However, the optimal combination regimen is not well established in elderly HT.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that combination therapy of telmisartan plus amlodipine would exert favorable cardiometabolic actions in elderly HT.
Methods: Seventeen elderly patients with essential HT who failed to achieve a target home BP level with treatment of 5 mg amlodipine plus 80 mg valsartan or 8 mg candesartan for at least 2 months were enrolled. Then the patients were assigned to replace their valsartan or candesartan with 40 mg telmisartan. The subjects were instructed to measure their own BP at home every day during the study periods.
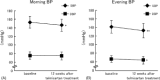
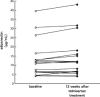
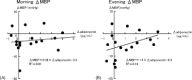
Results: Replacement of valsartan or candesartan by telmisartan in amlodipine-treated elderly hypertensive patients showed a significant reduction in morning home systolic BP and evening home systolic and diastolic BP at 12 weeks. Switching to telmisartan significantly increased serum adiponectin level.
Conclusions: Our present study suggests that combination therapy with telmisartan plus amlodipine may exert more beneficial cardiometabolic effects in elderly patients with HT compared with valsartan or candesartan plus amlodipine treatment.
© 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of combination therapy with telmisartan plus amlodipine in patients with poorly controlled hypertension.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2010 Sep-Oct;3(5):342-6. doi: 10.4161/oxim.3.5.13199. Epub 2010 Sep 1. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2010. PMID: 21150340 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effects of telmisartan and valsartan as add-on agents for hypertensive patients with morning blood pressure insufficiently controlled by amlodipine monotherapy.Hypertens Res. 2014 Mar;37(3):225-31. doi: 10.1038/hr.2013.141. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Hypertens Res. 2014. PMID: 24108237 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and duration of action of the four selective angiotensin II subtype 1 receptor blockers, losartan, candesartan, valsartan and telmisartan, in patients with essential hypertension determined by home blood pressure measurements.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2005 Aug;27(6):477-89. doi: 10.1081/CEH-200067668. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2005. PMID: 16081340
-
Amlodipine/valsartan single-pill combination: a review of its use in the management of hypertension.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2009;9(5):309-30. doi: 10.2165/11201120-000000000-00000. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19791840 Review.
-
Efficacy of fixed-dose combination therapy in the treatment of patients with hypertension: focus on amlodipine/valsartan.Clin Drug Investig. 2010;30(9):625-41. doi: 10.2165/11538440-000000000-00000. Clin Drug Investig. 2010. PMID: 20626210 Review.
Cited by
-
A review of the benefits of early treatment initiation with single-pill combinations of telmisartan with amlodipine or hydrochlorothiazide.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2013;9:521-8. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S48291. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2013. PMID: 24082785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and tolerability of telmisartan plus amlodipine in asian patients not adequately controlled on either monotherapy or on low-dose combination therapy.Int J Hypertens. 2014;2014:475480. doi: 10.1155/2014/475480. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Int J Hypertens. 2014. PMID: 24719757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- US Census Bureau . Estimated world population figures 2020. Available at: http://www.census.gov/ipc/www/idb/tables.html. Accessed April 13, 2009.
-
- Ogihara T, Kikuchi K, Matsuoka H, et al; Japanese Society of Hypertension Committee. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2009). Chapter 8. Hypertension in the elderly. Hypertension Res. 2009;32:57–62.
-
- Kostis JB. Antihypertensive therapy with CCB/ARB combination in older individuals: focus on amlodipine/valsartan combination. Am J Ther. 2010;17:188–196. - PubMed
-
- Turnbull F. Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists' Collaboration. Effects of different blood‐pressure‐lowering regimens on major cardiovascular events: results of prospectively‐designed overviews of randomised trials. Lancet. 2003;362: 1527–1535. - PubMed
-
- Arima H, Tanizaki Y, Kiyohara Y, et al. Validity of the JNC VI recommendations for the management of hypertension in a general population of Japanese elderly: the Hisayama study. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163:361–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

