Real-time optical motion correction for diffusion tensor imaging
- PMID: 21432898
- PMCID: PMC3139706
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.22787
Real-time optical motion correction for diffusion tensor imaging
Abstract
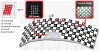
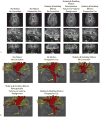
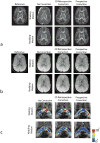
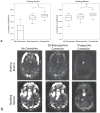
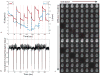
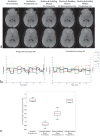
Head motion is a fundamental problem in brain MRI. The problem is further compounded in diffusion tensor imaging because of long acquisition times, and the sensitivity of the tensor computation to even small misregistration. To combat motion artifacts in diffusion tensor imaging, a novel real-time prospective motion correction method was introduced using an in-bore monovision system. The system consists of a camera mounted on the head coil and a self-encoded checkerboard marker that is attached to the patient's forehead. Our experiments showed that optical prospective motion correction is more effective at removing motion artifacts compared to image-based retrospective motion correction. Statistical analysis revealed a significant improvement in similarity between diffusion data acquired at different time points when prospective correction was used compared to retrospective correction (P<0.001).
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Rohde GK, Barnett AS, Basser PJ, Marenco S, Pierpaoli C. Comprehensive approach for correction of motion and distortion in diffusion-weighted MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2004;51(1):103–114. - PubMed
-
- Jiang S, Xue H, Counsell S, Anjari M, Allsop J, Rutherford M, Rueckert D, Hajnal JV. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of the brain in moving subjects: application to in-utero fetal and ex-utero studies. Magn Reson Med. 2009;62(3):645–655. - PubMed
-
- Leemans A, Jones DK. The B-matrix must be rotated when correcting for subject motion in DTI data. Magn Reson Med. 2009;61(6):1336–1349. - PubMed
-
- Pipe JG. Motion correction with PROPELLER MRI: application to head motion and free-breathing cardiac imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1999;42(5):963–969. - PubMed
-
- Liu C, Bammer R, Kim DH, Moseley ME. Self-navigated interleaved spiral (SNAILS): application to high-resolution diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2004;52(6):1388–1396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

