Thioredoxin interacting protein is a novel mediator of retinal inflammation and neurotoxicity
- PMID: 21434880
- PMCID: PMC3171869
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01336.x
Thioredoxin interacting protein is a novel mediator of retinal inflammation and neurotoxicity
Abstract
Background and purpose: Up-regulation of thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP), an endogenous inhibitor of thioredoxin (Trx), compromises cellular antioxidant and anti-apoptotic defences and stimulates pro-inflammatory cytokines expression, implying a role for TXNIP in apoptosis. Here we have examined the causal role of TXNIP expression in mediating retinal neurotoxicity and assessed the neuroprotective actions of verapamil, a calcium channel blocker and an inhibitor of TXNIP expression.
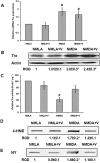
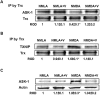
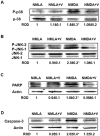
Experimental approach: Retinal neurotoxicity was induced by intravitreal injection of NMDA in Sprague-Dawley rats, which received verapamil (10 mg·kg(-1), p.o.) or vehicle. Neurotoxicity was examined by terminal dUTP nick-end labelling assay and ganglion cell count. Expression of TXNIP, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK-1), NF-κB, p38 MAPK, JNK, cleaved poly-ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP), caspase-3, nitrotyrosine and 4-hydroxy-nonenal were examined by Western and slot-blot analysis. Release of TNF-α and IL-1β was examined by elisa.
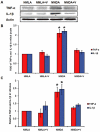
Key results: NMDA injection enhanced TXNIP expression, decreased Trx activity, causing increased oxidative stress, glial activation and release of TNF-α and IL-1β. Enhanced TXNIP expression disrupted Trx/ASK-1 inhibitory complex leading to release of ASK-1 and activation of the pro-apoptotic p38 MAPK/JNK pathway, as indicated by cleaved PARP and caspase-3 expression. Treatment with verapamil blocked these effects.
Conclusion and implications: Elevated TXNIP expression contributed to retinal neurotoxicity by three different mechanisms, inducing release of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α and IL-1β, altering antioxidant status and disrupting the Trx-ASK-1 inhibitory complex leading to activation of the p38 MAPK/JNK apoptotic pathway. Targeting TXNIP expression is a potential therapeutic target for retinal neurodegenerative disease.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures




References
-
- Abdelsaid MA, Pillai BA, Matragoon S, Prakash R, Al-Shabrawey M, El-Remessy AB. Early intervention of tyrosine nitration prevents vaso-obliteration and neovascularization in ischemic retinopathy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010;332:125–134. - PubMed
-
- Ali TK, Matragoon S, Pillai BA, Liou GI, El-Remessy AB. Peroxynitrite mediates retinal neurodegeneration by inhibiting NGF survival signal in experimental and human diabetes. J Diabetes. 2008;57:889–898. - PubMed
-
- Ali TK, Al-Gayyar MMH, Matragoon S, Pillai BA, Abdelsaid MA, Nussbaum JJ, et al. Diabetes-induced peroxynitrite impairs the balance of ProNGF/NGF and causes neurovascular injury. Diabetologia. 2011;54:657–668. - PubMed
-
- Arkan MC, Hevener AL, Greten FR, Maeda S, Li ZW, Long JM, et al. IKK-beta links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2005;11:191–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

