Factors associated with serum brain natriuretic peptide levels after the Fontan procedure
- PMID: 21435188
- PMCID: PMC3134550
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1747-0803.2011.00496.x
Factors associated with serum brain natriuretic peptide levels after the Fontan procedure
Abstract
Objective: Although a useful marker of heart failure in adults, the utility of brain natriuretic peptide concentration (BNP) for children after the Fontan procedure is not well studied.
Design: BNP was measured in 510 patients who were 6-18 years old in the Pediatric Heart Network Fontan cross-sectional study at a median of 8.2 years after Fontan. Patients underwent echocardiography, exercise testing, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and functional health status questionnaires. Associations of BNP with baseline patient characteristics, medical history and cross-sectional assessment were examined with multivariable linear regression analyses.
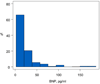
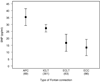
Results: The distribution of BNP was highly skewed, median 13.0 pg/mL (interquartile range: 7.1, 25.9), and was normalized with logarithmic transformation (logBNP). Among medical history variables, logBNP was greater in females (P= .02) and older patients (P < .001). Presence of pre-Fontan systolic ventricular dysfunction, greater number of post-Fontan complications, and thrombosis after Fontan were independently associated with higher logBNP (R(2) = 0.16). Age-adjusted logBNP was significantly related to Fontan connection type (lower with extracardiac conduits, higher with atriopulmonary connection; P < .001). Lower physical functioning health status (R(2) = 0.05), lower chronotropic index during exercise (R(2) = 0.17), indices of diastolic dysfunction measured by echocardiography (R(2) = 0.15), and higher total ventricular mass on MRI (R(2) = 0.33) were related to higher logBNP.
Conclusions: Despite a markedly abnormal circulation, BNP was variable but within a normal range in the majority of Fontan patients in this large outpatient cohort. Higher BNP was associated with several markers of suboptimal outcome, although associations were weak. The routine use of BNP as an outpatient surveillance tool in asymptomatic Fontan patients is not warranted.
© 2011 Copyright the Authors. Congenital Heart Disease © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Maisel AS, Clopton P, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, Duc P, Omland T, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, Wu AH, Steg G, Westheim A, Knudsen CW, Perez A, Kazanegra R, Bhalla V, Herrmann HC, Aumont MC, McCullough PA. Impact of age, race, and sex on the ability of B-type natriuretic peptide to aid in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure: results from the Breathing Not Properly (BNP) multinational study. Am Heart J. 2004;147:1078–1084. - PubMed
-
- Maisel AS, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, Duc P, Omland T, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, Wu AH, Clopton P, Steg PG, Westheim A, Knudsen CW, Perez A, Kazanegra R, Herrmann HC, McCullough PA. Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2002;18:161–167. - PubMed
-
- Law YM, Keller BB, Feingold BM, Boyle GJ. Usefulness of plasma B-type natriuretic peptide to identify ventricular dysfunction in pediatric and adult patients with congenital heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 2005;95:474–478. - PubMed
-
- Koch A, Zink S, Singer H. B-type natriuretic peptide in paediatric patients with congenital heart disease. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:861–866. - PubMed
-
- Anderson PA, Sleeper LA, Mahony L, Colan SD, Atz AM, Breitbart RE, Gersony WM, Gallagher D, Geva T, Margossian R, McCrindle BW, Paridon S, Schwartz M, Stylianou M, Williams RV, Clark BJ., III Contemporary outcomes after the Fontan procedure: a Pediatric Heart Network multicenter study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:85–98. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL068288/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068285/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068269/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068279/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL068270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068281/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068279/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068288/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068281/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068292/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068269/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068285/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068292/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

