Survival bias and drug interaction can attenuate cross-sectional case-control comparisons of genes with health outcomes. An example of the kinesin-like protein 6 (KIF6) Trp719Arg polymorphism and coronary heart disease
- PMID: 21435211
- PMCID: PMC3078850
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-12-42
Survival bias and drug interaction can attenuate cross-sectional case-control comparisons of genes with health outcomes. An example of the kinesin-like protein 6 (KIF6) Trp719Arg polymorphism and coronary heart disease
Abstract
Background: Case-control studies typically exclude fatal endpoints from the case set, which we hypothesize will substantially underestimate risk if survival is genotype-dependent. The loss of fatal cases is particularly nontrivial for studies of coronary heart disease (CHD) because of significantly reduced survival (34% one-year fatality following a coronary attack). A case in point is the KIF6 Trp719Arg polymorphism (rs20455). Whereas six prospective studies have shown that carriers of the KIF6 Trp719Arg risk allele have 20% to 50% greater CHD risk than non-carriers, several cross-sectional case-control studies failed to show that carrier status is related to CHD. Computer simulations were therefore employed to assess the impact of the loss of fatal events on gene associations in cross-sectional case-control studies, using KIF6 Trp719Arg as an example.
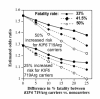
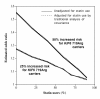
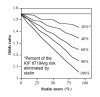
Results: Ten replicates of 1,000,000 observations each were generated reflecting Canadian demographics. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) risks were assigned by the Framingham equation and events distributed among KIF6 Trp719Arg genotypes according to published prospective studies. Logistic regression analysis was used to estimate odds ratios between KIF6 genotypes. Results were examined for 33%, 41.5%, and 50% fatality rates for incident CVD.In the absence of any difference in percent fatalities between genotypes, the odds ratios (carriers vs. noncarriers) were unaffected by survival bias, otherwise the odds ratios were increasingly attenuated as the disparity between fatality rates increased between genotypes. Additional simulations demonstrated that statin usage, shown in four clinical trials to substantially reduce the excess CHD risk in the KIF6 719Arg variant, should also attenuate the KIF6 719Arg odds ratio in case-control studies.
Conclusions: These computer simulations show that exclusions of prior CHD fatalities attenuate odds ratios of case-control studies in proportion to the difference in the percent fatalities between genotypes. Disproportionate CHD survival for KIF6 Trip719Arg carriers is suggested by their 50% greater risk for recurrent myocardial infarction. This, and the attenuation of KIF6 719Arg carrier risk with statin use, may explain the genotype's weak association with CHD in cross-sectional case-control studies. The results may be relevant to the underestimation of risk in cross-sectional case-control studies of other genetic CHD-risk factors affecting survival.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Meta-analyses of KIF6 Trp719Arg in coronary heart disease and statin therapeutic effect.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050126. Epub 2012 Dec 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23236363 Free PMC article.
-
KIF6 Trp719Arg polymorphism and the effect of statin therapy in elderly patients: results from the PROSPER study.Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2010 Aug;17(4):455-61. doi: 10.1097/HJR.0b013e328336a0dd. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2010. PMID: 20215968 Clinical Trial.
-
Association of the Trp719Arg polymorphism in kinesin-like protein 6 with myocardial infarction and coronary heart disease in 2 prospective trials: the CARE and WOSCOPS trials.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008 Jan 29;51(4):435-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.05.057. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18222353
-
The Trp719Arg polymorphism of the KIF6 gene and coronary heart disease risk: systematic review and meta-analysis.Hereditas. 2015 Oct 22;152:3. doi: 10.1186/s41065-015-0004-7. eCollection 2015. Hereditas. 2015. PMID: 28096762 Free PMC article.
-
KIF6 polymorphism as a predictor of risk of coronary events and of clinical event reduction by statin therapy.Am J Cardiol. 2010 Oct 1;106(7):994-8. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2010.05.033. Epub 2010 Aug 11. Am J Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20854963 Review.
Cited by
-
Using family members to augment genetic case-control studies of a life-threatening disease.Stat Med. 2016 Jul 20;35(16):2815-30. doi: 10.1002/sim.6888. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Stat Med. 2016. PMID: 26866629 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of CETP polymorphism on atorvastatin lipid-regulating effect and clinical prognosis of patients with coronary heart disease.Med Sci Monit. 2014 Dec 30;20:2824-9. doi: 10.12659/MSM.892711. Med Sci Monit. 2014. PMID: 25547030 Free PMC article.
-
The PPARγ2 Pro12Ala variant is protective against progression of nephropathy in people with type 2 diabetes.J Transl Med. 2015 Mar 12;13:85. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0448-6. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25889595 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analyses of KIF6 Trp719Arg in coronary heart disease and statin therapeutic effect.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050126. Epub 2012 Dec 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23236363 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variants in FBN-1 and risk for thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 17;9(4):e91437. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091437. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24743685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics--2011 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010. in press http://circ.ahajournals.org/cgi/reprint/CIR.0b013e3182009701v1. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

