Accumulated frailty characteristics predict postoperative discharge institutionalization in the geriatric patient
- PMID: 21435921
- PMCID: PMC3132184
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2011.01.056
Accumulated frailty characteristics predict postoperative discharge institutionalization in the geriatric patient
Abstract
Background: Frailty is a state of increased vulnerability to health-related stressors and can be measured by summing the number of frailty characteristics present in an individual. Discharge institutionalization (rather than discharge to home) represents disease burden and functional dependence after hospitalization. Our aim was to determine the relationship between frailty and need for postoperative discharge institutionalization.
Study design: Subjects ≥ 65 years undergoing major elective operations requiring postoperative ICU admission were enrolled. Discharge institutionalization was defined as need for institutionalized care at hospital discharge. Fourteen preoperative frailty characteristics were measured in 6 domains: comorbidity burden, function, nutrition, cognition, geriatric syndromes, and extrinsic frailty.
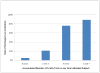
Results: A total of 223 subjects (mean age 73 ± 6 years) were studied. Discharge institutionalization occurred in 30% (n = 66). Frailty characteristics related to need for postoperative discharge institutionalization included: older age, Charlson index ≥ 3, hematocrit <35%, any functional dependence, up-and-go ≥ 15 seconds, albumin <3.4 mg/dL, Mini-Cog score ≤ 3, and having fallen within 6 months (p < 0.0001 for all comparisons). Multivariate logistic regression retained prolonged timed up-and-go (p < 0.0001) and any functional dependence (p < 0.0001) as the variables most closely related to need for discharge institutionalization. An increased number of frailty characteristics present in any one subject resulted in increased rate of discharge institutionalization.
Conclusions: Nearly 1 in 3 geriatric patients required discharge to an institutional care facility after major surgery. The frailty characteristics of prolonged up-and-go and any functional dependence were most closely related to the need for discharge institutionalization. Accumulation of a higher number of frailty characteristics in any one geriatric patient increased their risk of discharge institutionalization.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
Re: Accumulated frailty characteristics predict postoperative discharge institutionalization in the geriatric patient.J Urol. 2011 Dec;186(6):2304-5. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.08.111. Epub 2011 Oct 26. J Urol. 2011. PMID: 22078607 No abstract available.
-
Re: Accumulated frailty characteristics predict postoperative discharge institutionalization in the geriatric patient.J Urol. 2012 Oct;188(4):1213-4. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.06.107. Epub 2012 Aug 16. J Urol. 2012. PMID: 22971382 No abstract available.
References
-
- Geriatric Review Syllabus - A Core Curriculum in Geriatric Medicine. 6. New York: American Geriatrics Society; 2006.
-
- Buchner DM, Wagner EH. Preventing frail health. Clin Geriatr Med. 1992;8:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Robinson TN, Eiseman B, Wallace JI, Church SD. Redefining Geriatric Pre-Operative Assessment Using Frailty, Disability and Co-Morbidity. Ann Surg. 2009;250:449–455. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence VA, Hazuda HP, Cornell JE, et al. Functional independence after major abdominal surgery in the elderly. J Am Coll Surg. 2004;199:762–772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

