Elevated fibroblast growth factor 23 is a risk factor for kidney transplant loss and mortality
- PMID: 21436289
- PMCID: PMC3083317
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010080894
Elevated fibroblast growth factor 23 is a risk factor for kidney transplant loss and mortality
Abstract
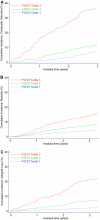
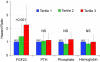
An increased circulating level of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) is an independent risk factor for mortality, cardiovascular disease, and progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD), but its role in transplant allograft and patient survival is unknown. We tested the hypothesis that increased FGF23 is an independent risk factor for all-cause mortality and allograft loss in a prospective cohort of 984 stable kidney transplant recipients. At enrollment, estimated GFR (eGFR) was 51 ± 21 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) and median C-terminal FGF23 was 28 RU/ml (interquartile range, 20 to 43 RU/ml). Higher FGF23 levels independently associated with increased risk of the composite outcome of all-cause mortality and allograft loss (full model hazard ratio: 1.46 per SD increase in logFGF23, 95% confidence interval: 1.28 to 1.68, P<0.001). The results were similar for each component of the composite outcome and in all sensitivity analyses, including prespecified analyses of patients with baseline eGFR of 30 to 90 ml/min per 1.73 m(2). In contrast, other measures of phosphorus metabolism, including serum phosphate and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels, did not consistently associate with outcomes. We conclude that a high (or elevated) FGF23 is an independent risk factor for death and allograft loss in kidney transplant recipients.
Copyright © 2011 by the American Society of Nephrology
Figures
Comment in
-
New insights to fibroblast growth factor 23 in kidney transplant.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011 May;22(5):799-801. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011020190. Epub 2011 Apr 7. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21474565 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wolfe RA, Ashby VB, Milford EL, Ojo AO, Ettenger RE, Agodoa LY, Held PJ, Port FK: Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N Engl J Med 341: 1725–1730, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Pascual M, Theruvath T, Kawai T, Tolkoff-Rubin N, Cosimi AB: Strategies to improve long-term outcomes after renal transplantation. N Engl J Med 346: 580–590, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Howard RJ, Patton PR, Reed AI, Hemming AW, Van der Werf WJ, Pfaff WW, Srinivas TR, Scornik JC: The changing causes of graft loss and death after kidney transplantation. Transplantation 73: 1923–1928, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

