β-catenin causes renal dysplasia via upregulation of Tgfβ2 and Dkk1
- PMID: 21436291
- PMCID: PMC3065227
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010050562
β-catenin causes renal dysplasia via upregulation of Tgfβ2 and Dkk1
Abstract
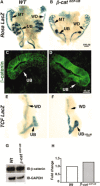
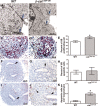
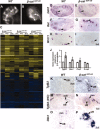
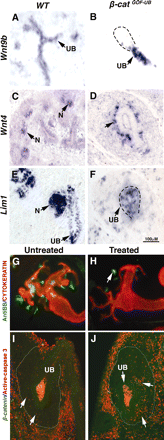
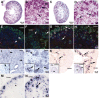
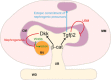
Renal dysplasia, defined by defective ureteric branching morphogenesis and nephrogenesis, is the major cause of renal failure in infants and children. Here, we define a pathogenic role for a β-catenin-activated genetic pathway in murine renal dysplasia. Stabilization of β-catenin in the ureteric cell lineage before the onset of kidney development increased β-catenin levels and caused renal aplasia or severe hypodysplasia. Analysis of gene expression in the dysplastic tissue identified downregulation of genes required for ureteric branching and upregulation of Tgfβ2 and Dkk1. Treatment of wild-type kidney explants with TGFβ2 or DKK1 generated morphogenetic phenotypes strikingly similar to those observed in mutant kidney tissue. Stabilization of β-catenin after the onset of kidney development also caused dysplasia and upregulation of Tgfβ2 and Dkk1 in the epithelium. Together, these results demonstrate that elevation of β-catenin levels during kidney development causes dysplasia.
Copyright © 2011 by the American Society of Nephrology
Figures


Comment in
-
β-Catenin: too much of a good thing is not always good.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011 Apr;22(4):592-3. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011020162. Epub 2011 Mar 24. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21436286 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
β-Catenin: too much of a good thing is not always good.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011 Apr;22(4):592-3. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011020162. Epub 2011 Mar 24. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21436286 No abstract available.
-
β-Catenin overexpression in the metanephric mesenchyme leads to renal dysplasia genesis via cell-autonomous and non-cell-autonomous mechanisms.Am J Pathol. 2014 May;184(5):1395-410. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.01.018. Epub 2014 Mar 15. Am J Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24637293
-
Canonical WNT/beta-catenin signaling is required for ureteric branching.Dev Biol. 2008 May 1;317(1):83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.02.010. Epub 2008 Feb 21. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18358465
-
The role of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in renal carcinogenesis: lessons from cadmium toxicity studies.Curr Mol Med. 2010 Jun;10(4):387-404. doi: 10.2174/156652410791316986. Curr Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20455852 Review.
-
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: a novel target for therapeutic intervention of fibrotic kidney disease.Arch Pharm Res. 2009 Dec;32(12):1653-62. doi: 10.1007/s12272-009-2200-3. Epub 2010 Feb 17. Arch Pharm Res. 2009. PMID: 20162391 Review.
Cited by
-
Renal Tubule Repair: Is Wnt/β-Catenin a Friend or Foe?Genes (Basel). 2018 Jan 24;9(2):58. doi: 10.3390/genes9020058. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29364168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the cellular and molecular landscapes of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in mouse embryonic kidney development.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024 Sep 2;23:3368-3378. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.08.025. eCollection 2024 Dec. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 39310276 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking TGF-β and β-Catenin Epithelial Crosstalk Exacerbates CKD.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Dec;28(12):3490-3503. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016121351. Epub 2017 Jul 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28701516 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-SID: Identifying EZH2 as a druggable target for desmoid tumors via in vivo dependency mapping.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Nov 23;118(47):e2115116118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2115116118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34789568 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental Origins for Kidney Disease Due to Shroom3 Deficiency.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Oct;27(10):2965-2973. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015060621. Epub 2016 Mar 3. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26940091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- N'Guessen G, Stephens FD, Pick J: Congenital superior ectopic (thoracic) kidney. Urology 24: 219–228, 1984 - PubMed
-
- Saxen L, Sariola H: Early organogenesis of the kidney. Pediatr Nephrol 1: 385–392, 1987 - PubMed
-
- Piscione TD, Rosenblum ND: The malformed kidney: Disruption of glomerular and tubular development. Clin Genet 56: 341–356, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Majumdar A, Vainio S, Kispert A, McMahon J, McMahon AP: Wnt11 and Ret/Gdnf pathways cooperate in regulating ureteric branching during metanephric kidney development. Development 130: 3175–3185, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Carroll TJ, Park JS, Hayashi S, Majumdar A, McMahon AP: Wnt9b plays a central role in the regulation of mesenchymal to epithelial transitions underlying organogenesis of the mammalian urogenital system. Dev Cell 9: 283–292, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

