Small intestine CD11c+ CD8+ T cells suppress CD4+ T cell-induced immune colitis
- PMID: 21436315
- PMCID: PMC3119121
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00032.2010
Small intestine CD11c+ CD8+ T cells suppress CD4+ T cell-induced immune colitis
Abstract
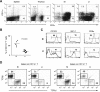
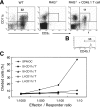
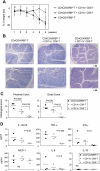
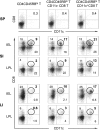
The large (LI) and small intestine (SI) differ in patterns of susceptibility to chronic mucosal inflammation. In this study, we evaluated whether this might, in part, reflect differences in resident mucosal CD11c(+) T cells. These cells comprised 39-48% (SI) and 12-17% (LI) of the intraepithelial compartment, most of which were T-cell receptor-αβ(+). In the SI, the majority of these cells were CD103(+) CD8(+) NK1.1(-), whereas the opposite phenotype prevailed in the LI. In transfer models of CD4(+) T cell-induced colitis, small numbers (2.5 × 10(5)) of SI CD11c(+) CD8(+) T cells suppressed proinflammatory cytokine-producing CD4(+) T cells in mesenteric lymph nodes and mucosa-associated lymphoid compartments (SI and LI) and protected mice from chronic inflammation. On a per-cell basis, the regulatory function of SI CD11c(+) T cells in CD4(+) T cell colitis was potent compared with other reported regulatory CD4(+) or CD8(+) T cells. In contrast, neither LI CD11c(+) T cells nor SI CD11c(-) T cells were effective in such immunoregulation. SI CD11c(+) CD8(+) T cells were similarly effective in suppressing CD4(+)CD45RB(hi) T cell colitis, as evidenced by inhibition of intracellular proinflammatory cytokine expression and histological inflammation. These findings indicate that SI CD11c(+) CD8(+) T cells are a distinct intestinal T cell population that plays an immunoregulatory role in control of proinflammatory CD4(+) T cells and maintenance of intestinal mucosal homeostasis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
B7 interactions with CD28 and CTLA-4 control tolerance or induction of mucosal inflammation in chronic experimental colitis.J Immunol. 2001 Aug 1;167(3):1830-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.3.1830. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11466409
-
Expression of dual TCR on DO11.10 T cells allows for ovalbumin-induced oral tolerance to prevent T cell-mediated colitis directed against unrelated enteric bacterial antigens.J Immunol. 2004 Feb 1;172(3):1515-23. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.3.1515. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14734729
-
Mesenteric B cells centrally inhibit CD4+ T cell colitis through interaction with regulatory T cell subsets.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 8;102(6):2010-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409449102. Epub 2005 Jan 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15684084 Free PMC article.
-
CD4(+) T-cell subsets in intestinal inflammation.Immunol Rev. 2013 Mar;252(1):164-82. doi: 10.1111/imr.12039. Immunol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23405904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights on CD8+ T Cells in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Therapeutic Approaches.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 11;12:738762. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.738762. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34707610 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oral Immunization with Attenuated Salmonella Choleraesuis Expressing the P42 and P97 Antigens Protects Mice against Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Challenge.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0236122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02361-22. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36377878 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effect of curcumin on experimental colitis mediated by inhibiting CD8+CD11c+ cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Mar 14;23(10):1804-1815. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i10.1804. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28348486 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary protein sources differentially affect microbiota, mTOR activity and transcription of mTOR signaling pathways in the small intestine.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 17;12(11):e0188282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188282. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29149221 Free PMC article.
-
Altered generation of induced regulatory T cells in the FVB.mdr1a-/- mouse model of colitis.Mucosal Immunol. 2013 Mar;6(2):309-23. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.73. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Mucosal Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22874899 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor β signaling controls activities of human intestinal CD8(+)T suppressor cells.Gastroenterology. 2013 Mar;144(3):601-612.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.12.001. Epub 2012 Dec 8. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23232296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allez M, Brimnes J, Dotan I, Mayer L. Expansion of CD8+ T cells with regulatory function after interaction with intestinal epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 123: 1516–1526, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Aranda R, Sydora BC, McAllister PL, Binder SW, Yang HY, Targan SR, Kronenberg M. Analysis of intestinal lymphocytes in mouse colitis mediated by transfer of CD4+, CD45RBhigh T cells to SCID recipients. J Immunol 158: 3464–3473, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Assarsson E, Kambayashi T, Sandberg JK, Hong S, Taniguchi M, Van Kaer L, Ljunggren HG, Chambers BJ. CD8+ T cells rapidly acquire NK1.1 and NK cell-associated molecules upon stimulation in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol 165: 3673–3679, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

