Protein phosphatase 2A B55 and A regulatory subunits interact with nitrate reductase and are essential for nitrate reductase activation
- PMID: 21436382
- PMCID: PMC3091043
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.111.172734
Protein phosphatase 2A B55 and A regulatory subunits interact with nitrate reductase and are essential for nitrate reductase activation
Abstract
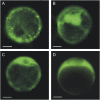
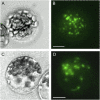
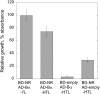
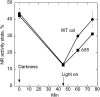
Posttranslational activation of nitrate reductase (NR) in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) and other higher plants is mediated by dephosphorylation at a specific Ser residue in the hinge between the molybdenum cofactor and heme-binding domains. The activation of NR in green leaves takes place after dark/light shifts, and is dependent on photosynthesis. Previous studies using various inhibitors pointed to protein phosphatases sensitive to okadaic acid, including protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), as candidates for activation of NR. PP2As are heterotrimeric enzymes consisting of a catalytic (C), structural (A), and regulatory (B) subunit. In Arabidopsis there are five, three, and 18 of these subunits, respectively. By using inducible artificial microRNA to simultaneously knock down the three structural subunits we show that PP2A is necessary for NR activation. The structural subunits revealed overlapping functions in the activation process of NR. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation was used to identify PP2A regulatory subunits interacting with NR, and the two B55 subunits were positive. Interactions of NR and B55 were further confirmed by the yeast two-hybrid assay. In Arabidopsis the B55 group consists of the close homologs B55α and B55β. Interestingly, the homozygous double mutant (b55α × b55β) appeared to be lethal, which shows that the B55 group has essential functions that cannot be replaced by other regulatory subunits. Mutants homozygous for mutation in Bβ and heterozygous for mutation in Bα revealed a slower activation rate for NR than wild-type plants, pointing to these subunits as part of a PP2A complex responsible for NR dephosphorylation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunits are starting to reveal their functions in plant metabolism and development.Plant Signal Behav. 2011 Aug;6(8):1216-8. doi: 10.4161/psb.6.8.16180. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2011. PMID: 21758015 Free PMC article.
-
Light regulation of nitrate reductase by catalytic subunits of protein phosphatase 2A.Planta. 2017 Oct;246(4):701-710. doi: 10.1007/s00425-017-2726-4. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Planta. 2017. PMID: 28656346
-
Antagonistic regulation of flowering time through distinct regulatory subunits of protein phosphatase 2A.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 26;8(7):e67987. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067987. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23976921 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct Clades of Protein Phosphatase 2A Regulatory B'/B56 Subunits Engage in Different Physiological Processes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 31;24(15):12255. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512255. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism and importance of post-translational regulation of nitrate reductase.J Exp Bot. 2004 Jun;55(401):1275-82. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erh132. Epub 2004 Apr 23. J Exp Bot. 2004. PMID: 15107452 Review.
Cited by
-
Systems analysis of transcriptome data provides new hypotheses about Arabidopsis root response to nitrate treatments.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Feb 7;5:22. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00022. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24570678 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive activation of nitrate reductase in tobacco alters flowering time and plant biomass.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 19;11(1):4222. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83797-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33608646 Free PMC article.
-
The effector AWR5 from the plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum is an inhibitor of the TOR signalling pathway.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 3;6:27058. doi: 10.1038/srep27058. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27257085 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of bacterial-like phosphoprotein phosphatases in photosynthetic eukaryotes features ancestral mitochondrial or archaeal origin and possible lateral gene transfer.Plant Physiol. 2013 Dec;163(4):1829-43. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.224378. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24108212 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of PP2A gene family in Camellia sinensis reveals the potential role of CsPP2A-TON2/FASS1 in abiotic stress.PeerJ. 2025 May 27;13:e19431. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19431. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40452937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al. (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Boudsocq M, Droillard MJ, Barbier-Brygoo H, Laurière C. (2007) Different phosphorylation mechanisms are involved in the activation of sucrose non-fermenting 1 related protein kinases 2 by osmotic stresses and abscisic acid. Plant Mol Biol 63: 491–503 - PubMed
-
- Buchanan BB, Gruissem W, Jones RL. (2000) Biochemistry & Molecular Biology of Plants. American Society of Plant Physiologists, Rockville, MD
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

