AMP-activated protein kinase regulates neuronal polarization by interfering with PI 3-kinase localization
- PMID: 21436401
- PMCID: PMC3325765
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1201678
AMP-activated protein kinase regulates neuronal polarization by interfering with PI 3-kinase localization
Abstract
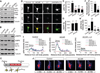
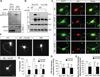
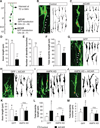
Axon-dendrite polarization is crucial for neural network wiring and information processing in the brain. Polarization begins with the transformation of a single neurite into an axon and its subsequent rapid extension, which requires coordination of cellular energy status to allow for transport of building materials to support axon growth. We found that activation of the energy-sensing adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway suppressed axon initiation and neuronal polarization. Phosphorylation of the kinesin light chain of the Kif5 motor protein by AMPK disrupted the association of the motor with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), preventing PI3K targeting to the axonal tip and inhibiting polarization and axon growth.
Figures

References
-
- Sabina RL, Patterson D, Holmes EW. J. Biol. Chem. 1985;260:6107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

