Upregulated stromal EGFR and vascular remodeling in mouse xenograft models of angiogenesis inhibitor-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 21436589
- PMCID: PMC3070607
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI42405
Upregulated stromal EGFR and vascular remodeling in mouse xenograft models of angiogenesis inhibitor-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
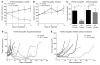
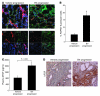
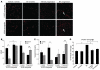
Angiogenesis is critical for tumor growth and metastasis, and several inhibitors of angiogenesis are currently in clinical use for the treatment of cancer. However, not all patients benefit from antiangiogenic therapy, and those tumors that initially respond to treatment ultimately become resistant. The mechanisms underlying this, and the relative contributions of tumor cells and stroma to resistance, are not completely understood. Here, using species-specific profiling of mouse xenograft models of human lung adenocarcinoma, we have shown that gene expression changes associated with acquired resistance to the VEGF inhibitor bevacizumab occurred predominantly in stromal and not tumor cells. In particular, components of the EGFR and FGFR pathways were upregulated in stroma, but not in tumor cells. Increased activated EGFR was detected on pericytes of xenografts that acquired resistance and on endothelium of tumors with relative primary resistance. Acquired resistance was associated with a pattern of pericyte-covered, normalized revascularization, whereas tortuous, uncovered vessels were observed in relative primary resistance. Importantly, dual targeting of the VEGF and EGFR pathways reduced pericyte coverage and increased progression-free survival. These findings demonstrated that alterations in tumor stromal pathways, including the EGFR and FGFR pathways, are associated with, and may contribute to, resistance to VEGF inhibitors and that targeting these pathways may improve therapeutic efficacy. Understanding stromal signaling may be critical for developing biomarkers for angiogenesis inhibitors and improving combination regimens.
Figures





Comment in
-
The adaptive stroma joining the antiangiogenic resistance front.J Clin Invest. 2011 Apr;121(4):1244-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI46430. Epub 2011 Mar 23. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21436579 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Triple inhibition of EGFR, Met, and VEGF suppresses regrowth of HGF-triggered, erlotinib-resistant lung cancer harboring an EGFR mutation.J Thorac Oncol. 2014 Jun;9(6):775-83. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000170. J Thorac Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24828661 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted therapy of orthotopic human lung cancer by combined vascular endothelial growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling blockade.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Feb;6(2):471-83. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0416. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17308046
-
Molecular basis of the synergistic antiangiogenic activity of bevacizumab and mithramycin A.Cancer Res. 2007 May 15;67(10):4878-85. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3494. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17510417
-
Combined inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor and epidermal growth factor signaling in non-small-cell lung cancer therapy.Clin Lung Cancer. 2009 Mar;10 Suppl 1:S17-23. doi: 10.3816/CLC.2009.s.003. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19362942 Review.
-
Dual targeting of the vascular endothelial growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptor pathways: rationale and clinical applications for non-small-cell lung cancer.Clin Lung Cancer. 2007 Feb;8 Suppl 2:S79-85. doi: 10.3816/clc.2007.s.006. Clin Lung Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17382029 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Transcriptome and Binding Sites Analyses Identify Early FOX Expressions for Enhancing Cardiomyogenesis Efficiency of hESC Cultures.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 9;6:31068. doi: 10.1038/srep31068. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27501774 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting angiogenesis in lung cancer - Pitfalls in drug development.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2012 Jun;1(2):122-8. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2012.01.01. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 25806168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic markers of DNA repair and PI3K pathway activation predict response to the PARP inhibitor BMN 673 in small cell lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Nov 15;19(22):6322-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1975. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24077350 Free PMC article.
-
SiRNA targeting EGFR effectively prevents posterior capsular opacification after cataract surgery.Mol Vis. 2011;17:2349-55. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 21921987 Free PMC article.
-
Brain derived neutrophic factor (BDNF) coordinates lympho-vascular metastasis through a fibroblast-governed paracrine axis in the tumor microenvironment.Cancer Cell Microenviron. 2017;4(2):e1566. doi: 10.14800/ccm.1566. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Cancer Cell Microenviron. 2017. PMID: 28966935 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

