Receptor crosstalk: haloperidol treatment enhances A(2A) adenosine receptor functioning in a transfected cell model
- PMID: 21437008
- PMCID: PMC3033501
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-010-9201-z
Receptor crosstalk: haloperidol treatment enhances A(2A) adenosine receptor functioning in a transfected cell model
Abstract
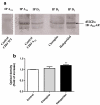
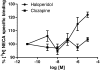
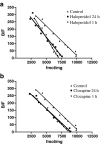
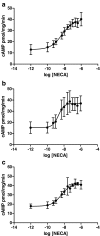
A(2A) adenosine receptors are considered an excellent target for drug development in several neurological and psychiatric disorders. It is noteworthy that the responses evoked by A(2A) adenosine receptors are regulated by D(2) dopamine receptor ligands. These two receptors are co-expressed at the level of the basal ganglia and interact to form functional heterodimers. In this context, possible changes in A(2A) adenosine receptor functional responses caused by the chronic blockade/activation of D(2) dopamine receptors should be considered to optimise the therapeutic effectiveness of dopaminergic agents and to reduce any possible side effects. In the present paper, we investigated the regulation of A(2A) adenosine receptors induced by antipsychotic drugs, commonly acting as D(2) dopamine receptor antagonists, in a cellular model co-expressing both A(2A) and D(2) receptors. Our data suggest that the treatment of cells with the classical antipsychotic haloperidol increased both the affinity and responsiveness of the A(2A) receptor and also affected the degree of A(2A)-D(2) receptor heterodimerisation. In contrast, an atypical antipsychotic, clozapine, had no effect on A(2A) adenosine receptor parameters, suggesting that the two classes of drugs have different effects on adenosine-dopamine receptor interaction. Modifications to A(2A) adenosine receptors may play a significant role in determining cerebral adenosine effects during the chronic administration of antipsychotics in psychiatric diseases and may account for the efficacy of A(2A) adenosine receptor ligands in pathologies associated with dopaminergic system dysfunction.
Electronic supplementary material: The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s11302-010-9201-z) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: A2A adenosine receptors; A2A binding parameters; D2 dopamine receptor antagonists; Receptor crosstalk; Receptor functioning.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of A2A adenosine receptors in platelets from patients affected by bipolar disorders under treatment with typical antipsychotics.J Psychiatr Res. 2006 Feb;40(1):81-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2004.12.008. J Psychiatr Res. 2006. PMID: 16431220
-
Molecular and behavioral effects mediated by Gs-coupled adenosine A2a, but not serotonin 5-Ht4 or 5-Ht6 receptors following antipsychotic administration.Neuroscience. 1999 Mar;89(3):927-38. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(98)00364-9. Neuroscience. 1999. PMID: 10199625
-
Effect of subtype-selective adenosine receptor antagonists on basal or haloperidol-regulated striatal function: studies of exploratory locomotion and c-Fos immunoreactivity in outbred and A(2A)R KO mice.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Jun 15;247:217-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.03.035. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23557694
-
Dysfunctional brain dopamine systems induced by psychotomimetic NMDA-receptor antagonists and the effects of antipsychotic drugs.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000 Mar;31(2-3):320-9. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(99)00048-x. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000. PMID: 10719159 Review.
-
The importance of the adenosine A(2A) receptor-dopamine D(2) receptor interaction in drug addiction.Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(3):317-55. doi: 10.2174/092986712803414231. Curr Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22335511 Review.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of adenosine A2A receptors induced by atypical antipsychotics and its correlation with sensory gating in schizophrenia patients.Psychiatry Res. 2012 Dec 30;200(2-3):126-32. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2012.04.021. Epub 2012 Jun 16. Psychiatry Res. 2012. PMID: 22705363 Free PMC article.
-
3-(Fur-2-yl)-10-(2-phenylethyl)-[1,2,4]triazino[4,3-a]benzimidazol-4(10H)-one, a novel adenosine receptor antagonist with A(2A)-mediated neuroprotective effects.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011 Sep 21;2(9):526-35. doi: 10.1021/cn200036s. Epub 2011 Jun 10. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22860174 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Heterodimerization between the G Protein-Coupled Receptor GPR17 and the Chemokine Receptors 2 and 4: New Evidence.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 23;24(1):261. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010261. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613703 Free PMC article.
-
Haloperidol-Associated Uterine Dystonia.Am J Psychiatry. 2017 Mar 1;174(3):296. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2016.16070800. Am J Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28245696 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Allosteric Interactions between Adenosine A2A and Dopamine D2 Receptors in Heteromeric Complexes: Biochemical and Pharmacological Characteristics, and Opportunities for PET Imaging.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 9;22(4):1719. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041719. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33572077 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

