Pleiotropic effects of rosuvastatin on microvascular function in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 21437072
- PMCID: PMC3047994
Pleiotropic effects of rosuvastatin on microvascular function in type 2 diabetes
Abstract
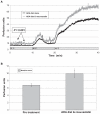
Rosuvastatin is known to reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol and improve endothelial function. In addition to lipid-lowering, statins may exert pleiotropic (nonlipid lowering) effects on microvascular function. We compared the neurophysiological and vascular responses of dietary control and treatment with 10 mg of rosuvastatin in 16 subjects with neuropathy and established type 2 diabetes. Skin blood flow (SkBF) measurements were measured at baseline, after 18 weeks of diet, and after 18 weeks of diet and treatment with rosuvastatin in response to local warming and ischemia reperfusion. The study results show that total cholesterol (196.50 ± 8.02 to 134.88 ± 10.86 mg/dL) and LDL-cholesterol (114 ± 10.4 to 63.4 ± 8.48 mg/dL) decreased significantly after 18 weeks of rosuvastatin, but not after 18 weeks of diet. Neuropathy scores decreased from 8.34 ± 1.26 at baseline to 6.00 ± 0.90 after rosuvastatin treatment. Basal SkBF was significantly different from baseline, 6.81 ± 0.42 to 9.92 ± 0.78 after rosuvastatin treatment (P ≤ 0.001). These results indicate that rosuvastatin therapy positively changed basal SkBF and measures of neurovascular function. Although there was a profound lipid lowering, it is not clear that this mediated the increases in SkBF and decreases in neuropathy scores.
Keywords: diabetes; neurovascular function; rosuvastatin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A 12-week, prospective, open-label analysis of the effect of rosuvastatin on triglyceride-rich lipoprotein metabolism in patients with primary dyslipidemia.Clin Ther. 2007 Jul;29(7):1403-14. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.07.019. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 17825691 Clinical Trial.
-
Rosuvastatin 5 and 10 mg/d: a pilot study of the effects in hypercholesterolemic adults unable to tolerate other statins and reach LDL cholesterol goals with nonstatin lipid-lowering therapies.Clin Ther. 2006 Jun;28(6):933-42. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2006.06.004. Clin Ther. 2006. PMID: 16860175 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of rosuvastatin on fasting and postprandial endothelial biomarker levels and microvascular reactivity in patients with type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia: a preliminary report.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017 Nov 9;16(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0629-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017. Retraction in: Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019 Mar 16;18(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0841-1. PMID: 29121934 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Pleiotropic effects of statins: evidence against benefits beyond LDL-cholesterol lowering.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2010;10 Suppl 1:10-7. doi: 10.2165/1158822-S0-000000000-00000. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2010. PMID: 21391729 Review.
-
Looking to the future: diabetic neuropathy and effects of rosuvastatin on neurovascular function in diabetes models.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2003 Jul;61 Suppl 1:S35-9. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8227(03)00123-2. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2003. PMID: 12880693 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of rosuvastatin and/or β-carotene on non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats.Res Pharm Sci. 2015 Jul-Aug;10(4):275-87. Res Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 26600855 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic effects of rosuvastatin on the glucose metabolism and the subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue behavior in C57Bl/6 mice.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2013 Jul 1;5(1):32. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-5-32. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2013. PMID: 23816341 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of rosuvastatin on diabetic polyneuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase IIa study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2014 Sep 4;7:401-7. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S65500. eCollection 2014. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2014. PMID: 25214797 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin on high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and lipid profile in obese type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2011 Oct;2(4):261-5. doi: 10.4103/0976-500X.85954. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2011. PMID: 22025854 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vinik AI, Erbas T, Park TS. Methods for evaluation of peripheral neurovascular dysfunction. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2001;3:29–50. - PubMed
-
- Vinik A, Erbas T, Park T, Stansberry K, Scanelli J, Pittenger G. Dermal neurovascular dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:1468–1475. - PubMed
-
- Holzer SE, Camerota A, Martens L, Cuerdon T, Crystal-Peters J, Zagari M. Costs and duration of care for lower extremity ulcers in patients with diabetes. Clin Ther. 1998;20:169–181. - PubMed
-
- Lloret R, Ycas J, Stein M, Haffner S. Comparison of rosuvastatin versus atorvastatin in Hispanic-Americans with hypercholesterolemia (from the STARSHIP trial) Am J Cardiol. 2006;98:768–773. - PubMed
-
- Bullano MF, Kamat S, Wertz DA, et al. Effectiveness of rosuvastatin versus atorvastatin in reducing lipid levels and achieving lowdensity- lipoprotein cholesterol goals in a usual care setting. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007;64:276–284. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
