A Regenerative Antioxidant Protocol of Vitamin E and α-Lipoic Acid Ameliorates Cardiovascular and Metabolic Changes in Fructose-Fed Rats
- PMID: 21437191
- PMCID: PMC3062110
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/120801
A Regenerative Antioxidant Protocol of Vitamin E and α-Lipoic Acid Ameliorates Cardiovascular and Metabolic Changes in Fructose-Fed Rats
Abstract
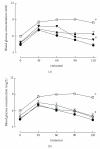
Type 2 diabetes is a major cause of cardiovascular disease. We have determined whether the metabolic and cardiovascular changes induced by a diet high in fructose in young adult male Wistar rats could be prevented or reversed by chronic intervention with natural antioxidants. We administered a regenerative antioxidant protocol using two natural compounds: α-lipoic acid together with vitamin E (α-tocopherol alone or a tocotrienol-rich fraction), given as either a prevention or reversal protocol in the food. These rats developed glucose intolerance, hypertension, and increased collagen deposition in the heart together with an increased ventricular stiffness. Treatment with a fixed combination of vitamin E (either α-tocopherol or tocotrienol-rich fraction, 0.84 g/kg food) and α-lipoic acid (1.6 g/kg food) normalized glucose tolerance, blood pressure, cardiac collagen deposition, and ventricular stiffness in both prevention and reversal protocols in these fructose-fed rats. These results suggest that adequate antioxidant therapy can both prevent and reverse the metabolic and cardiovascular damage in type 2 diabetes.
Figures


References
-
- Miller A, Adeli K. Dietary fructose and the metabolic syndrome. Current Opinion in Gastroenterology. 2008;24(2):204–209. - PubMed
-
- Vasdev S, Longerich L, Gill V. Prevention of fructose-induced hypertension by dietary vitamins. Clinical Biochemistry. 2004;37(1):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Lee O, Bruce WR, Dong Q, Bruce J, Mehta R, O’Brien PJ. Fructose and carbonyl metabolites as endogenous toxins. Chemico-Biological Interactions. 2009;178(1–3):332–339. - PubMed
-
- Abdullah MM, Riediger NN, Chen Q, et al. Effects of long-term consumption of a high-fructose diet on conventional cardiovascular risk factors in sprague-dawley rats. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 2009;327(1-2):247–256. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

