Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) gene polymorphisms are not associated with sarcoidosis in the Japanese population
- PMID: 21437199
- PMCID: PMC3062517
Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) gene polymorphisms are not associated with sarcoidosis in the Japanese population
Abstract
Purpose: Sarcoidosis is a systemic inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of non-caseating granulomas, with varied clinical manifestations. The common etiology of sarcoidosis is uncertain, but it is thought to be triggered by an exogenous antigenic stimulus, such as some bacterial proteins. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) recognize microbial components and elicit innate as well as adaptive immune responses. It has been reported that polymorphisms in TLR2 might be important in a small group of Caucasian sarcoidosis patients. The present study aimed to establish whether these findings are relevant to the Japanese population.
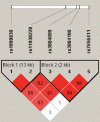
Methods: We genotyped 5 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in TLR2 and assessed the allelic diversity between 257 Japanese sarcoidosis patients and 193 Japanese healthy controls.
Results: No significant differences in the frequency of TLR2 alleles and haplotypes in the sarcoidosis cases were found in comparison with the controls. However, marginal associations were observed for TLR2 at rs3804099 and rs3804100 in sarcoidosis patients with cutaneous manifestations.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that TLR2 polymorphisms are not significantly related to the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis in the Japanese population.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lack of association between toll-like receptor 4 gene polymorphisms and sarcoidosis-related uveitis in Japan.Mol Vis. 2009 Dec 10;15:2673-82. Mol Vis. 2009. PMID: 20011079 Free PMC article.
-
Association of toll-like receptor 2 gene polymorphisms with normal tension glaucoma.Mol Vis. 2009 Dec 26;15:2905-10. Mol Vis. 2009. PMID: 20057905 Free PMC article.
-
Association between genetic polymorphisms of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and schizophrenia in the Korean population.Gene. 2013 Sep 10;526(2):182-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.04.058. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23644137
-
Association of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in toll-like receptor 2 gene with asthma susceptibility: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 May;96(20):e6822. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006822. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28514297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Japanese single nucleotide polymorphism database for 267 possible drug-related genes.Cancer Sci. 2006 Jan;97(1):16-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00142.x. Cancer Sci. 2006. PMID: 16367916 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Toll-like receptor 2 polymorphisms with papillary thyroid cancer and clinicopathologic features in a Korean population.J Korean Med Sci. 2012 Nov;27(11):1333-8. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.11.1333. Epub 2012 Oct 30. J Korean Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 23166414 Free PMC article.
-
Disordered Toll-like receptor 2 responses in the pathogenesis of pulmonary sarcoidosis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2013 Sep;173(3):512-22. doi: 10.1111/cei.12138. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23668840 Free PMC article.
-
Etiologies of Sarcoidosis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015 Aug;49(1):6-18. doi: 10.1007/s12016-015-8481-z. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25771769 Review.
-
Sarcoidosis vs. Sarcoid-like reactions: The Two Sides of the same Coin?Wien Med Wochenschr. 2014 Jul;164(13-14):247-59. doi: 10.1007/s10354-014-0269-x. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2014. PMID: 24664574 Review.
References
-
- Newman LS, Rose CS, Maier LA. Sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1224–34. - PubMed
-
- Baughman RP, Lower EE, du Bois RM. Sarcoidosis. Lancet. 2003;361:1111–8. - PubMed
-
- Iannuzzi MC, Rybicki BA, Teirstein AS. Sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2153–65. - PubMed
-
- ACCESS Research Group Design of a case control etiologic study of sarcoidosis (ACCESS). J Clin Epidemiol. 1999;52:1173–86. - PubMed
-
- Morimoto T, Azuma A, Abe S, Usuki J, Kudoh S, Sugisaki K, Oritsu M, Nukiwa T. Epidemiology of sarcoidosis in Japan. Eur Respir J. 2008;31:372–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
