The Notch-2 gene is regulated by Wnt signaling in cultured colorectal cancer cells
- PMID: 21437251
- PMCID: PMC3060910
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017957
The Notch-2 gene is regulated by Wnt signaling in cultured colorectal cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Notch and Wnt pathways are key regulators of intestinal homeostasis and alterations in these pathways may lead to the development of colorectal cancer (CRC). In CRC the Apc/β-catenin genes in the Wnt signaling pathway are frequently mutated and active Notch signaling contributes to tumorigenesis by keeping the epithelial cells in a proliferative state. These pathways are simultaneously active in proliferative adenoma cells and a crosstalk between them has previously been suggested in normal development as well as in cancer.
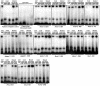
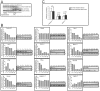
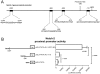
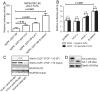
Principal findings: In this study, in silico analysis of putative promoters involved in transcriptional regulation of genes coding for proteins in the Notch signaling pathway revealed several putative LEF-1/TCF sites as potential targets for β-catenin and canonical Wnt signaling. Further results from competitive electrophoretic mobility-shift assay (EMSA) studies suggest binding of several putative sites in Notch pathway gene promoters to in vitro translated β-catenin/Lef-1. Wild type (wt)-Apc negatively regulates β-catenin. By induction of wt-Apc or β-catenin silencing in HT29 cells, we observed that several genes in the Notch pathway, including Notch-2, were downregulated. Finally, active Notch signaling was verified in the Apc(Min/+) mouse model where Hes-1 mRNA levels were found significantly upregulated in intestinal tumors compared to normal intestinal mucosa. Luciferase assays showed an increased activity for the core and proximal Notch-2 promoter upon co-transfection of HCT116 cells with high expression recombinant Tcf-4, Lef-1 or β-catenin.
Conclusions: In this paper, we identified Notch-2 as a novel target for β-catenin-dependent Wnt signaling. Furthermore our data supports the notion that additional genes in the Notch pathway might be transcriptionally regulated by Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sox17 modulates Wnt3A/beta-catenin-mediated transcriptional activation of the Lef-1 promoter.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010 Nov;299(5):L694-710. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00140.2010. Epub 2010 Aug 27. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20802155 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic exchange of TCF3 and TCF4 transcription factors controls MYC expression in colorectal cancer cells.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(3):323-32. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.980643. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25659031 Free PMC article.
-
OVOL2, an Inhibitor of WNT Signaling, Reduces Invasive Activities of Human and Mouse Cancer Cells and Is Down-regulated in Human Colorectal Tumors.Gastroenterology. 2016 Mar;150(3):659-671.e16. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.11.041. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Gastroenterology. 2016. PMID: 26619963
-
[In situ analyses of molecular mechanisms of colorectal carcinogenesis].Pathologe. 2013 Nov;34 Suppl 2:269-73. doi: 10.1007/s00292-013-1821-y. Pathologe. 2013. PMID: 24196627 Review. German.
-
Transcriptional Regulation of Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Colorectal Cancer.Cells. 2020 Sep 19;9(9):2125. doi: 10.3390/cells9092125. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32961708 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia, notch signalling, and prostate cancer.Nat Rev Urol. 2013 Jul;10(7):405-13. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2013.110. Epub 2013 May 28. Nat Rev Urol. 2013. PMID: 23712204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs as the critical regulators of epithelial mesenchymal transition in colorectal tumor cells: an overview.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Feb 10;22(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02501-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35144601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notch and Hedgehog Signaling Unveiled: Crosstalk, Roles, and Breakthroughs in Cancer Stem Cell Research.Life (Basel). 2025 Feb 4;15(2):228. doi: 10.3390/life15020228. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40003637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notch and Wnt Dysregulation and Its Relevance for Breast Cancer and Tumor Initiation.Biomedicines. 2018 Nov 1;6(4):101. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines6040101. Biomedicines. 2018. PMID: 30388742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Desmoid Tumors: Current Perspective and Treatment.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2024 Feb;25(2):161-175. doi: 10.1007/s11864-024-01177-5. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38270798 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Es JH, Clevers H. Notch and Wnt inhibitors as potential new drugs for intestinal neoplastic disease. Trends Mol Med. 2005;11:496–502. - PubMed
-
- Crosnier C, Stamataki D, Lewis J. Organizing cell renewal in the intestine: stem cells, signals and combinatorial control. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:349–359. - PubMed
-
- Kelleher FC, Fennelly D, Rafferty M. Common critical pathways in embryogenesis and cancer. Acta Oncol. 2006;45:375–388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

