Neutrophil interactions with sialyl Lewis X on human nonsmall cell lung carcinoma cells regulate invasive behavior
- PMID: 21437888
- PMCID: PMC3134589
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.26059
Neutrophil interactions with sialyl Lewis X on human nonsmall cell lung carcinoma cells regulate invasive behavior
Abstract
Background: The carbohydrate sialyl Lewis X (sLeX) is expressed on leukocytes and carcinoma cells and binds to selectins during inflammatory processes and early metastasis. Synthesis of sLeX depends on activity of enzymes, including α(1,3/1,4) fucosyltransferase (FucT-III). Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) up-regulates FucT-III, resulting in increased sLeX in the airways of patients with respiratory disease; however, the mechanisms that regulate sLeX in the inflammatory tumor microenvironment are not well understood.
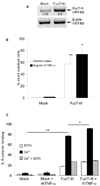
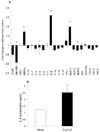
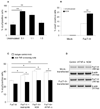
Methods: The authors stably transfected human lung carcinoma cell lines with the FucT-III gene and exposed them to TNF-α to investigate its role in regulation of sLeX expression and selectin-binding ability using semiquantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and flow cytometry. Cytokine expression was examined in transfected cells using chemiluminescent arrays and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, and invasion was studied using Matrigel assays and alterations in morphology. Human lung tissue arrays were analyzed for immunohistochemical detection of sLeX and neutrophils.
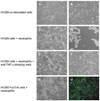
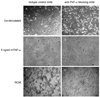
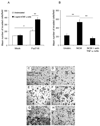
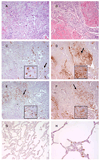
Results: Stimulation of FucT-III-transfected cells with recombinant human (rh) TNF-α up-regulated sLeX expression and increased E-selectin binding. Transfected cells secreted high levels of interleukin 8, growth-regulated oncogene-α, and mast cell proteinase-1. Cells exposed to rhTNF-α, neutrophil-conditioned media, and cultures with a 5:1 ratio of neutrophils to cancer cells had significantly increased sLeX expression and invasiveness and underwent nonadherent morphologic changes. In lung carcinomas, but not in normal lung tissues, 71% of tumors were highly positive for sLeX expression in areas of increased neutrophil infiltration.
Conclusions: The current results indicated that neutrophils may be recruited to areas of FucT-III activity and sLeX expression in lung carcinomas to enhance the invasive and metastatic potential of lung cancer cells.
Copyright © 2011 American Cancer Society.
Figures
References
-
- Coello MC, Luketich JD, Litle VR, et al. Prognostic significance of micrometastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2004;5:214–225. - PubMed
-
- Nakamori S, Kameyama M, Imaoka S, et al. Increased expression of sialyl Lewisx antigen correlates with poor survival in patients with colorectal carcinoma: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study. Cancer Res. 1993;53:3632–3637. - PubMed
-
- Izumi Y, Kawamura YJ, Irimura T. Carbohydrate antigens in carcinoma invasion and metastasis. Nippon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996;97:140–144. - PubMed
-
- Ogawa JI, Inoue H, Koide S. alpha-2,3-Sialyltransferase type 3N and alpha-1,3-fucosyltransferase type VII are related to sialyl Lewis(x) synthesis and patient survival from lung carcinoma. Cancer. 1997;79:1678–1685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

