Effects of attentional load on early visual processing depend on stimulus timing
- PMID: 21438076
- PMCID: PMC6870163
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.21193
Effects of attentional load on early visual processing depend on stimulus timing
Abstract
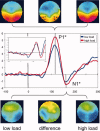
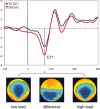
A growing number of studies suggest that early visual processing is not only affected by low-level perceptual attributes but also by higher order cognitive factors such as attention or emotion. Using high-density electroencephalography, we recently demonstrated that attentional load of a task at fixation reduces the response of primary visual cortex to irrelevant peripheral stimuli, as indexed by the C1 component. In the latter study, peripheral stimuli were always presented during intervals without task-relevant stimuli. Here, we use a similar paradigm but present central task stimuli and irrelevant peripheral stimuli simultaneously while keeping all other stimulus characteristics constant. Results show that rather than to suppress responses to peripheral stimulation, high attentional load elicits higher C1 amplitudes under these conditions. These findings suggest that stimulus timing can profoundly alter the effects of attentional load on the earliest stages of processing in human visual cortex.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Amunts K, Malikovic A, Mohlberg H, Schormann T, Zilles K ( 2000): Brodmann's areas 17 and 18 brought into stereotaxic space—Where and how variable? Neuroimage 11: 66–84. - PubMed
-
- Bahcall DO, Kowler E ( 1999): Attentional interference at small spatial separations. Vis Res 39: 71–86. - PubMed
-
- Blake R, Lee S‐H ( 2005): The role of temporal structure in human vision. Behav Cogn Neurosci Rev 4: 21–42. - PubMed
-
- Brefczynski JA, DeYoe EA ( 1999): A physiological correlate of the ‘spotlight’ of visual attention. Nat Neurosci 2: 370–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

