Identification of inhibitors that block vaccinia virus infection by targeting the DNA synthesis processivity factor D4
- PMID: 21438571
- PMCID: PMC3155816
- DOI: 10.1021/jm101554k
Identification of inhibitors that block vaccinia virus infection by targeting the DNA synthesis processivity factor D4
Abstract
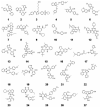
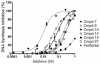
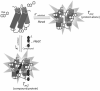
Smallpox was globally eradicated 30 years ago by vaccination. The recent threat of bioterrorism demands the development of improved vaccines and novel therapeutics to effectively preclude a reemergence of smallpox. One new therapeutic target is the vaccinia poxvirus processivity complex, comprising D4 and A20 proteins that enable the viral E9 DNA polymerase to synthesize extended strands. Five compounds identified from an AlphaScreen assay designed to disrupt A20:D4 binding were shown to be effective in: (i) blocking vaccinia processive DNA synthesis in vitro, (ii) preventing cellular infection with minimal cytotoxicity, and (iii) binding to D4, as evidenced by ThermoFluor. The EC(50) values for inhibition of viral infectivity ranged from 9.6 to 23 μM with corresponding selectivity indices (cytotoxicity CC(50)/viral infectivity EC(50)) of 3.9 to 17.8. The five compounds are thus potential therapeutics capable of halting smallpox DNA synthesis and infectivity through disruptive action against a component of the vaccinia processivity complex.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of polymerase and processivity inhibitors of vaccinia DNA synthesis using a stepwise screening approach.Antiviral Res. 2008 Nov;80(2):114-23. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2008.05.010. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Antiviral Res. 2008. PMID: 18621425 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of protein-protein interaction inhibitors targeting vaccinia virus processivity factor for development of antiviral agents.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Nov;55(11):5054-62. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00278-11. Epub 2011 Aug 15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21844323 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the role of the vaccinia virus uracil DNA glycosylase and A20 proteins as intrinsic components of the DNA polymerase holoenzyme.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 15;286(28):24702-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.222216. Epub 2011 May 13. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21572084 Free PMC article.
-
The vaccinia virus DNA polymerase and its processivity factor.Virus Res. 2017 Apr 15;234:193-206. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2017.01.027. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 28159613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poxvirus uracil-DNA glycosylase-An unusual member of the family I uracil-DNA glycosylases.Protein Sci. 2016 Dec;25(12):2113-2131. doi: 10.1002/pro.3058. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Protein Sci. 2016. PMID: 27684934 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Crystal structure of the vaccinia virus DNA polymerase holoenzyme subunit D4 in complex with the A20 N-terminal domain.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Mar 6;10(3):e1003978. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003978. eCollection 2014 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24603707 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes Simplex Virus-1 infection in human primary corneal epithelial cells is blocked by a stapled peptide that targets processive DNA synthesis.Ocul Surf. 2021 Jan;19:313-321. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2020.11.001. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Ocul Surf. 2021. PMID: 33161128 Free PMC article.
-
Collaborative virtual screening to elaborate an imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine hit series for visceral leishmaniasis.RSC Med Chem. 2021 Jan 21;12(3):384-393. doi: 10.1039/d0md00353k. RSC Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34041487 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of DNA Glycosylases as Prospective Drugs.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 28;21(9):3118. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093118. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32354123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of core therapeutic targets for Monkeypox virus and repurposing potential of drugs: A WEB prediction approach.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 6;19(12):e0303501. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303501. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39642129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Longini IM, Jr, Halloran ME, Nizam A, Yang Y, Xu S, Burke DS, Cummings DA, Epstein JM. Containing a large bioterrorist smallpox attack: a computer simulation approach. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2007;11:98–108. - PubMed
-
- Kong XP, Onrust R, O’Donnell M, Kuriyan J. Three-dimensional structure of the beta subunit of E. coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme: a sliding DNA clamp. Cell. 1992;69:425–437. - PubMed
-
- Krishna TS, Kong XP, Gary S, Burgers PM, Kuriyan J. Crystal structure of the eukaryotic DNA polymerase processivity factor PCNA. Cell. 1994;79:1233–1243. - PubMed
-
- Ellison V, Stillman B. Opening of the clamp: an intimate view of an ATP-driven biological machine. Cell. 2001;106:655–660. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical

