Lipidomics at the interface of structure and function in systems biology
- PMID: 21439472
- PMCID: PMC3132894
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.01.014
Lipidomics at the interface of structure and function in systems biology
Abstract
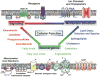
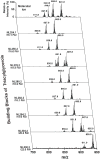
Cells, tissues, and biological fluids contain a diverse repertoire of many tens of thousands of structurally distinct lipids that play multiple roles in cellular signaling, bioenergetics, and membrane structure and function. In an era where lipid-related disease states predominate, lipidomics has assumed a prominent role in systems biology through its unique ability to directly identify functional alterations in multiple lipid metabolic and signaling networks. The development of shotgun lipidomics has led to the facile accrual of high density information on alterations in the lipidome mediating physiologic cellular adaptation during health and pathologic alterations during disease. Through both targeted and nontargeted investigations, lipidomics has already revealed the chemical mechanisms underlying many lipid-related disease states.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bartz R, Li W-H, Venables B, Zehmer JK, Roth MR, Welti R, Anderson RG, Liu P, Chapman KD. Lipidomics reveals that adiposomes store ether lipids and mediate phospholipid traffic. J Lipid Res. 2007;48:837–847. - PubMed
-
- Beckonert O, Coe M, Keun HC, Wang Y, Ebbels TMD, Holmes E, Lindon JC, Nicholson JK. High-resolution magic-angle-spinning NMR spectroscopy for metabolic profiling of intact tissues. Nat Protoc. 2010;5:1019–1032. - PubMed
-
- Breen EP, Gouin SG, Murphy AF, Haines LR, Jackson AM, Pearson TW, Murphy PV, Porter RK. On the mechanism of mitochondrial uncoupling protein 1 function. J Biol Chem. 2005;281:2114–2119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

